Updated: 10/16/23
Do you suffer from liver failure? If so, you are far from alone. It is estimated that nearly 400 million people in the world are affected by some form of chronic liver disease. But there is hope! Liver failure can be reversed with proper diet and supplementation – if detected early enough. In this blog post we will dive into the symptoms, risk factors and dietary changes related to dealing with liver failure while exploring how nutritional supplements can help reverse the damage done to your body. Don’t let liver disease take control of your life – start restoring balance today!
What is Liver Failure?
The liver is the largest gland in the human body. It is crucial for protein production and filtering waste products. The liver creates bile for digestion, detoxifies the body and stores sugar and fat as energy. When the liver doesn’t function properly, it can affect the whole body. Liver failure occurs when large portions of the liver become damaged beyond repair, making it difficult for the liver to function. Liver failure is a life-threatening condition. Research indicates that about 30 million people in the U.S. suffer from liver disease.
Most often, liver failure is a chronic condition, meaning it develops gradually over many years. However, the condition may also be acute and the liver fails very rapidly. Some of the most common factors that lead to chronic liver failure are hepatitis infections and alcohol consumption that cause scarring in liver tissue. Common causes for acute liver failure include drugs, exposure to toxins, infections and metabolic disorders.
Is Liver Failure Fatal?
Liver failure is a serious medical condition that can be fatal if left untreated. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment of liver failure can help you prevent the condition or seek prompt medical care in the event of a diagnosis. By taking steps to reduce your risk of liver damage, such as avoiding excessive alcohol consumption and practicing safe sex, you can help protect your liver and maintain good health. If you experience any symptoms of liver failure, it is important to seek immediate medical attention to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
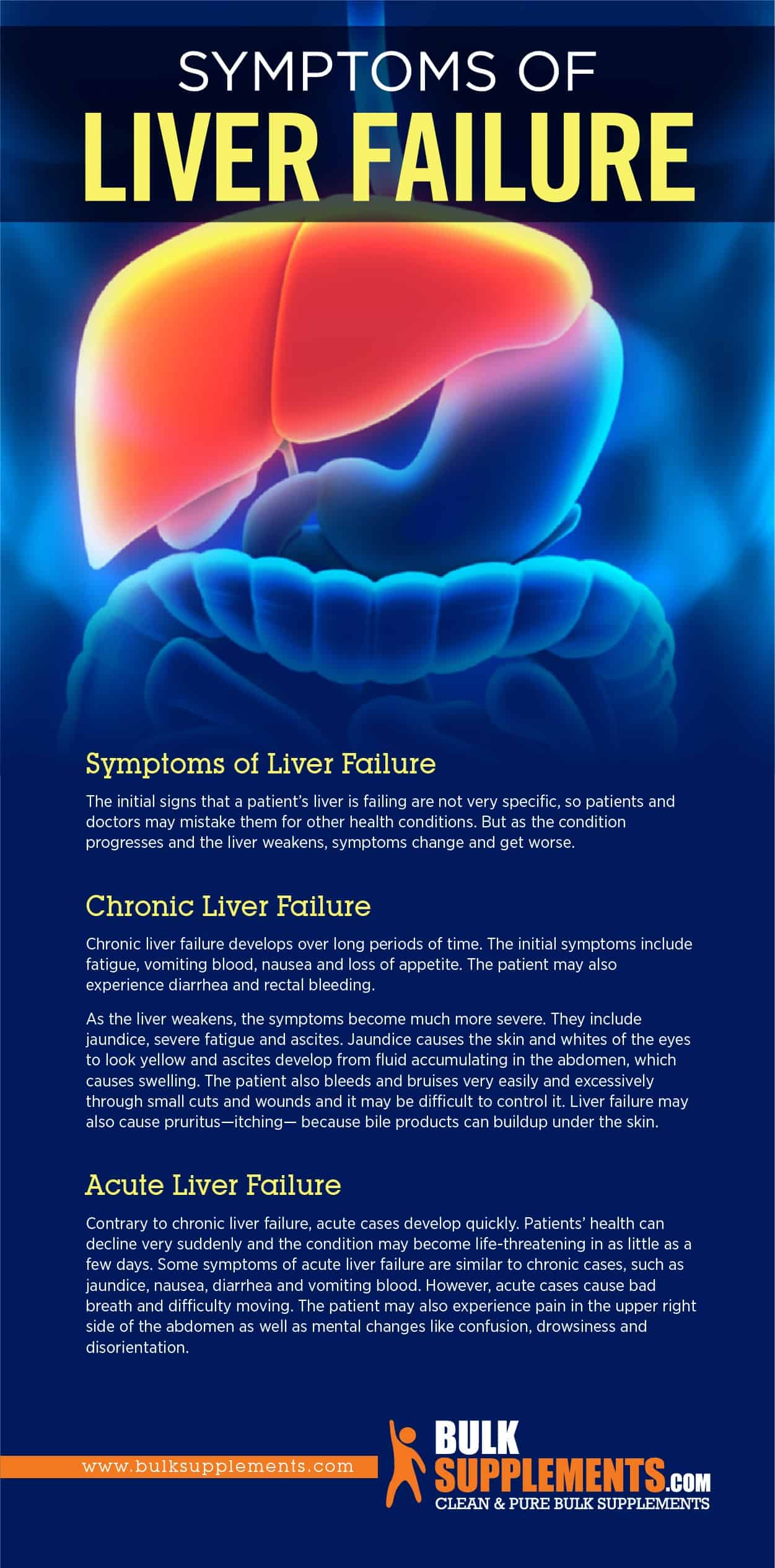
Symptoms of Liver Failure
The initial signs that a patient’s liver is failing are not very specific, so patients and doctors may mistake them for other health conditions. But as the condition progresses and the liver weakens, symptoms change and get worse.
Jaundice
One of the most common symptoms of liver failure is jaundice, a condition that turns your skin and whites of your eyes yellow. This condition occurs when the liver fails to filter bilirubin, a waste product produced during the breakdown of old red blood cells. If you notice yellowing of the skin or eyes, you must consult your doctor immediately.
Swelling
Liver failure can also cause abdominal pain and swelling. This occurs because the liver plays a crucial role in processing nutrients, hormones, and other substances in the blood. When it fails to do so, it can lead to fluid buildup in the abdomen, which can cause swelling and discomfort.
Gastrointestinal issues
Liver failure can wreak havoc on the digestive system, causing nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and indigestion. You may also experience a loss of appetite, weight loss, and a general feeling of weakness and fatigue.
Changes in Mental State
In severe cases, liver failure can lead to changes in mental state, such as confusion, slurred speech, and even coma. This occurs because the liver plays a crucial role in filtering toxins from the blood, including those that affect brain function. As a result, a buildup of toxins can cause changes in mental state and may require emergency medical attention.
Easy bruising and bleeding
The liver produces clotting factors that help stop bleeding when you get injured. In liver failure, the liver may not produce enough clotting factors, leading to easy bruising and bleeding. You may also notice frequent nosebleeds or bleeding gums.
Stages of Liver Failure
Acute Liver Failure
Contrary to chronic liver failure, acute cases develop quickly. Patients’ health can decline very suddenly and the condition may become life-threatening in as little as a few days. Some symptoms of acute liver failure are similar to chronic cases, such as jaundice, nausea, diarrhea and vomiting blood. However, acute cases cause bad breath and difficulty moving. The patient may also experience pain in the upper right side of the abdomen as well as mental changes like confusion, drowsiness and disorientation.
Chronic Liver Failure
Chronic liver failure develops over long periods of time. The initial symptoms include fatigue, vomiting blood, nausea and loss of appetite. The patient may also experience diarrhea and rectal bleeding.
As the liver weakens, the symptoms become much more severe. They include jaundice, severe fatigue and ascites. Jaundice causes the skin and whites of the eyes to look yellow and ascites develop from fluid accumulating in the abdomen, which causes swelling. The patient also bleeds and bruises very easily and excessively through small cuts and wounds and it may be difficult to control it. Liver failure may also cause pruritus—itching— because bile products can buildup under the skin.
What is End Stage Liver Failure?
End stage liver failure occurs when the liver is no longer able to function properly, and its ability to regenerate and repair itself is severely compromised. The most common causes of end-stage liver failure are chronic hepatitis B and C infections, excessive alcohol consumption, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, autoimmune hepatitis, and inherited liver diseases such as hemochromatosis, Wilson’s disease, and alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency.
Causes of Liver Failure
Liver failure can be a silent killer, and it’s essential to understand its causes to prevent it. Liver failure can be prevented by living a healthy lifestyle, being vaccinated against hepatitis, and seeking early treatment for autoimmune liver disease. If you’re a heavy drinker or taking medications, it’s essential to monitor the dosage and seek medical advice if you suspect any liver damage. By taking preventative measures, you can protect your liver and live a long and healthy life.
Alcohol Abuse
The liver’s filtering capacity cannot sustain a heavy or prolonged intake of alcohol. Continued alcohol abuse can eventually lead to liver inflammation, scarring, and cirrhosis. The amount and duration of alcohol consumption decide the severity of liver damage. It is advised that men should limit their alcohol consumption to two drinks a day, while women should stick to only one. Anyone who has trouble limiting their alcohol intake should seek professional help.
Hepatitis Infection
Hepatitis B and C are viral infections that can cause chronic liver disease. These viruses are transmitted through contaminated blood or body fluids from infected individuals. The presence of the HBV (Hepatitis B Virus) or HCV (Hepatitis C Virus) causes inflammation of the liver cells, which can lead to cirrhosis, liver cancer, and liver failure. To prevent hepatitis, one should practice safe sex, avoid sharing needles and infected objects, and get vaccinated against hepatitis A and B.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a condition where excess fat builds up in the liver cells. The leading cause of NAFLD is obesity, high blood sugar levels, insulin resistance, and unhealthy diet choices. Initially, NAFLD does not cause any significant symptoms but can eventually lead to liver inflammation, cirrhosis, and liver failure, if left untreated. It is essential to maintain a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and maintain a healthy weight to avoid this condition.
Autoimmune Diseases
An autoimmune disease occurs when our immune system attacks the body’s healthy cells, mistaking them for foreign substances. Autoimmune hepatitis is a rare condition that causes chronic inflammation and scarring of the liver tissue. Women and young adults are more susceptible to the disease. The condition’s treatment is with immune-suppressants and lifestyle changes such as losing weight and limiting alcohol consumption.
Autoimmune Liver Disease
Your immune system can turn against your body, leading to autoimmune liver disease. Three major types of autoimmune liver disease include autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis, and primary sclerosing cholangitis. These autoimmune diseases cause inflammation and scarring of the liver, eventually leading to liver failure. Although the cause of autoimmune liver disease is unknown, it’s crucial to seek treatment early to prevent further damage.
Medication and Drug Overdose
The liver plays an essential role in metabolizing and purifying drugs and medications from our body. An overdose of medications such as acetaminophen can cause severe liver damage that can lead to liver failure. It is important to read medication labels thoroughly, avoid improper dosing, and consult a healthcare professional before taking any medication.
Liver Failure with Kidney Failure
The liver and the kidneys are two vital organs in the human body that work together to keep the body healthy and functioning correctly. These two organs filter toxins from the blood and maintain the body’s balance. However, sometimes one of these organs may fail or become damaged, leading to a significant impact on the other organ’s functioning.
The liver and kidneys share a close connection, and the failure of one may lead to the failure of the other. Liver failure is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the liver cannot perform its basic functions. The liver is responsible for removing toxins from the blood, producing bile, and storing nutrients, among other things. When liver failure occurs, toxins build up in the blood, and the body cannot function correctly.
How Liver Disease is Diagnosed
Doctors diagnose liver failure by evaluating the patient’s symptoms with a physical exam. The doctor also performs a blood test to measure enzymes and liver function, followed by other blood tests, urine tests and a chest x-ray to look for complications. The doctor will also try to figure out the cause of the condition by asking the patient about prescription and over-the-counter drugs, as well as alcohol and illicit drug use.
Can Liver Failure be Reversed?
The liver is a unique organ that can regenerate its lost tissue. And, liver failure can be reversed if the condition is treated in the early stages. The liver’s ability to regenerate varies from person to person, and it depends on the age, general health, and severity of the liver failure. But, if the liver is severely damaged, regeneration may not occur.
Treatment for Liver Failure
Treatment for liver failure depends on the underlying cause and whether the condition is acute or chronic. Doctors advise different dietary restrictions to protect the liver and the patient may even require a liver transplant. In acute cases, the patient needs immediate treatment. Without treatment, liver failure can be fatal. It can cause complications in the body like jaundice, kidney failure and gastrointestinal bleeding from varicose veins and even hepatic encephalopathy that affects the brain.
Lifestyle Changes
The first step in treating liver failure is making necessary lifestyle changes, such as avoiding alcohol, regular exercise and following a healthy diet. These changes can help to improve liver function and reverse mild liver damage. To improve the liver function, you should consume more fresh vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats and avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and fatty foods. Moreover, staying physically active can also help reduce liver fat, increase insulin sensitivity, and improve blood sugar levels.
Medications
The use of certain medications may be initiated to manage conditions that cause acute liver failure. For instance, acyclovir is a medication to manage herpes infections, which cause acute liver failure. In some situations, medications such as corticosteroids are given to manage an autoimmune disorder, as autoimmune hepatitis, which may also result in acute liver failure.
Intravenous Glucose
Intravenous glucose is administered to patients with acute liver failure to manage hypoglycemia which usually accompanies liver failure. Glucose is to produce energy by the body, and the liver is an essential organ that stores glucose. However, with acute liver failure, the liver loses the ability to perform this function leading to low blood sugar. Intravenous glucose replenishes the lost glucose and aids in the management of the condition.
Dialysis
The kidneys to which the liver is adjacent may also be affected by acute liver failure leading to a build-up of toxins in the blood. Dialysis is a blood purification process to filter the blood and remove toxins. Dialysis may be used in patients with acute liver failure suffering from kidney failure.
Nutritional Support
In advanced stages of liver failure, patients may require nutritional support. Nutritional support can help to maintain optimal health by supplying the body with essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and proteins. This support may be provided through a feeding tube or intravenous (IV) line.
Alternative Therapies
Some alternative therapies such as herbal remedies, supplements, and acupuncture have claimed to help improve liver health and reverse damage in liver failure patients. However, there is not much scientific evidence to support the effectiveness of these therapies in treating liver failure. Moreover, before trying any alternative therapies, it is essential to discuss the potential benefits and risks with a healthcare professional.
Supportive Care
As the patient recovers, supportive care is provided to them to manage the complications of acute liver failure. Supportive care involves the management of symptoms such as pain, nausea, fatigue, and fluid build-up in the body. The aim is to manage the symptoms and support the patient through the recovery phase.
Liver Transplant
Liver transplant is the most effective treatment option for acute liver failure. Here, a healthy liver from a donor is transplanted into the patient to replace the failed liver. However, given the severity of the condition, liver transplant needs to be urgent as the patient may not survive without the procedure. The patient receives a new, healthy liver from a liver or deceased donor. The surgeon may replace the entire liver or just a portion of it because it may be able to grow back.
Preventing Liver Failure
Making healthy lifestyle choices can help prevent organ damage. Patients can help reduce the risk by taking actions to protect themselves from the causes. For example:
- Limiting alcohol & avoid drug abuse
- Following prescription instructions
- Eat a balanced diet
- Exercise regularly
- Getting vaccinations for hepatitis
- Practice safe sex
Supplements for Liver Failure
Natural dietary supplements may be able to benefit overall health and prevent liver damage. However, they are not a cure for any medical condition. Always consult a doctor before starting a supplement regimen to avoid complications.
Dandelion Root
Dandelion root comes from the common dandelion, which has an array of nutrients and health benefits. For example, it can help reduce inflammation in the body from oxidative stress and possibly prevent chronic diseases. It also contains inulin, which maintains proper bile flow. The suggested serving for dandelion root extract powder is 1,000 mg (about ⅓ tsp) twice a day, or following a doctor’s instructions.
Alpha Lipoic Acid (ALA)
Alpha lipoic acid (ALA) is an organic compound that converts nutrients into energy. According to research, it is present in several different healthy foods and even has antioxidant properties to reduce inflammation in the body. ALA may also be able to help patients lose weight in order to manage the effects of liver damage. The recommended dosage for alpha lipoic acid (ALA) powder is 600 mg (about ¼ tsp) once or twice daily with meals. Do not take too much at once because it may interfere with natural ALA levels in the body.
Milk Thistle
Milk thistle is native to Europe and for more than 2,000 years people have used it for its healing properties. Specifically, it may address liver problems and possibly improve fatty liver disease. Research also states that milk thistle may be able to protect the body from hepatitis. All of these factors may be beneficial to patients at risk for liver failure. As a dietary supplement, take 250 mg (about ⅛ tsp) of milk thistle extract powder per day, after consulting a physician for approval.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is an important nutrient that plays a vital role in protecting the liver from damage. It is a powerful antioxidant that helps to protect liver cells from free radical damage, and has shown to improve liver function in people with NAFLD. Additionally, research has shown that vitamin E supplements can help reduce inflammation in the liver, which is beneficial for people with liver disease.
Artichoke Extract
Despite appearances, artichokes are actually part of the daisy family. They contain antioxidants that can fight disease and signs of aging. Artichokes also help protect the liver. Research states that it may be able to help reduce fat deposits and inflammation in fatty liver disease. As a dietary supplement, take 700 mg of artichoke extract powder per day, if a physician approves the dosage.
Turmeric
Turmeric is a type of ginger and a very popular spice. One of its main components is curcumin. It has antioxidant properties that help neutralize free radicals that cause disease. Curcumin can also help reduce inflammation in the liver, which can help protect it from damage. As a dietary supplement, take no more than 1,000 mg of turmeric root extract powder a day with food or water. Roughly, 1,000 mg is about ½ tsp or a little more than ⅜ tsp. Consult a doctor before taking this product to ensure safety.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil and other sources, can help reduce inflammation in the liver and improve liver function. They can also help reduce the risk of liver fibrosis, a condition where the liver becomes scarred and stiff. Omega-3 fatty acids also have cardiovascular benefits, which is important since people with liver failure are at increased risk of heart disease.
Berberine
Berberine is an alkaloid found in various plants, including goldenseal and barberry. It has been used for centuries in traditional Chinese medicine to treat various ailments, including liver disease. Studies have shown that berberine supplements can reduce inflammation in the liver and improve liver function tests in people with liver disease.
The Bottom Line
The liver is a vital organ that plays a crucial role in our overall health. It detoxifies harmful substances from our body, purifies our blood, and helps digest food. Liver failure is a life-threatening condition that can occur when the liver loses its ability to function properly. Although it exists by various factors, including viral infections, alcohol abuse, and drug overdose; it is preventable with good habits and proper care.
Liver failure is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention, and natural supplements should never be a substitute for medical treatment. However, incorporating these supplements into your diet under the guidance of a healthcare professional may help improve liver function and speed up the recovery process. Milk thistle, N-Acetyl Cysteine, turmeric, vitamin E, and dandelion root are just a few of the best supplements for liver failure that have been backed by science. If you suspect you’re suffering from liver failure, make sure to speak to your healthcare provider before taking any supplements.
Treatment options include dietary and lifestyle changes or a liver transplant. One way patients can prevent liver failure by protecting the body from damage is to make sure they receive adequate amounts of nutrients from food or supplements. However, it is always best to consult a doctor about liver failure and any other medical conditions. Lifestyle changes and supplements are not a cure, but research claims that they can help benefit overall health.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease