Updated: 10/12/23
Are you concerned about the growing prevalence of fatty liver disease? Up to 25% of adults in the US suffer from this dangerous, yet highly preventable condition. If you’re worried that changes to your lifestyle and diet could put you at risk for fatty liver, then it’s time to make sure you get the supplements necessary for prevention. BulkSupplements.com offers a wide variety of supplements specifically targeted at preventing, and even reversing fatty liver disease, allowing health-conscious individuals the chance to reduce their chances for developing the condition without having to reach for pharmaceuticals or surgery. Keep on reading and find out how bulk supplements can help keep your liver happy!
What is Fatty Liver Disease?
Fatty liver disease is a condition where there’s an accumulation of excess fat in the liver tissue. It’s estimated that up to a quarter of the population has some degree of fatty liver disease, and it’s becoming more common due to the rise in obesity and unhealthy lifestyle choices. There are two main types of fatty liver disease: alcoholic fatty liver and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Alcoholic fatty liver is caused by excessive alcohol consumption. It’s reversible if caught early and if alcohol consumption is stopped. NAFLD, on the other hand, is more prevalent and is not caused by alcohol consumption. It’s often associated with metabolic issues like obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes, and high blood pressure.
Moderate drinkers and even those who refrain from alcohol can also develop fatty liver disease. Studies assert how one in four people in America suffer from fatty liver disease. Many people with this condition are often unaware that they have it or even what the condition truly entails.
Fatty liver disease has mild symptoms in many cases. However, it can also cause life-threatening complications in severe cases. Fortunately, lifestyle changes can reverse the condition. Experts do not entirely know why some people contract it and others do not. However, the main risk factors for fatty liver disease involve hypertension, hepatitis C, diabetes, high blood cholesterol and liver infections. Although most people with this condition are older adults, it can affect anyone at any age.
Types of Fatty Liver Disease
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common type of fatty liver disease, affecting millions of people worldwide. NAFLD is a condition where the liver accumulates excess fat, despite the absence of alcohol consumption. NAFLD is commonly seen in people who are overweight, obese, and suffer from metabolic disorders like type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance. Symptoms of NAFLD include fatigue, abdominal pain, and mild jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD)
Alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) is a condition where an excess amount of fat accumulates in the liver due to excessive alcohol consumption. AFLD can cause liver inflammation, liver scarring, and liver failure if not detected early and treated adequately. Symptoms of AFLD include abdominal pain, fatigue, and an enlarged liver.
Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a more severe form of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). This condition is characterized by liver inflammation and liver cell damage, which can progress to liver cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer. NASH is closely associated with obesity, high blood sugar levels and insulin resistance, and high cholesterol levels. Symptoms of NASH include fatigue, abdominal pain, and an enlarged liver.
Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy (AFLP)
Acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP) is a rare but serious complication that occurs during pregnancy. This condition is characterized by an excess accumulation of fat in the liver, causing inflammation and liver cell damage. AFLP can lead to liver failure, kidney failure, and even maternal and fetal death if not treated immediately. Symptoms of AFLP include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and jaundice.
Fatty Liver Disease Caused by Medications
Certain medications can cause liver damage, leading to fatty liver disease. The medications commonly linked to this condition include steroids, tamoxifen, and methotrexate, among others. This type of fatty liver disease can go unnoticed for years and can be diagnosed only through imaging scans or liver biopsies. The initial treatment entails stopping the medication causing the condition. Further treatment depends on the severity of the liver damage and may include medications or surgery.
Fatty Liver Disease Symptoms
Fatty liver disease often does not produce any symptoms. However, if symptoms appear, they normally relate to the following:
- A sensation of being full in the middle and upper right of the abdomen
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Jaundice
- Muscle weakness
- Edema
- Confusion
- Fatigue
- Red palms
- Enlarged blood vessels under the skin
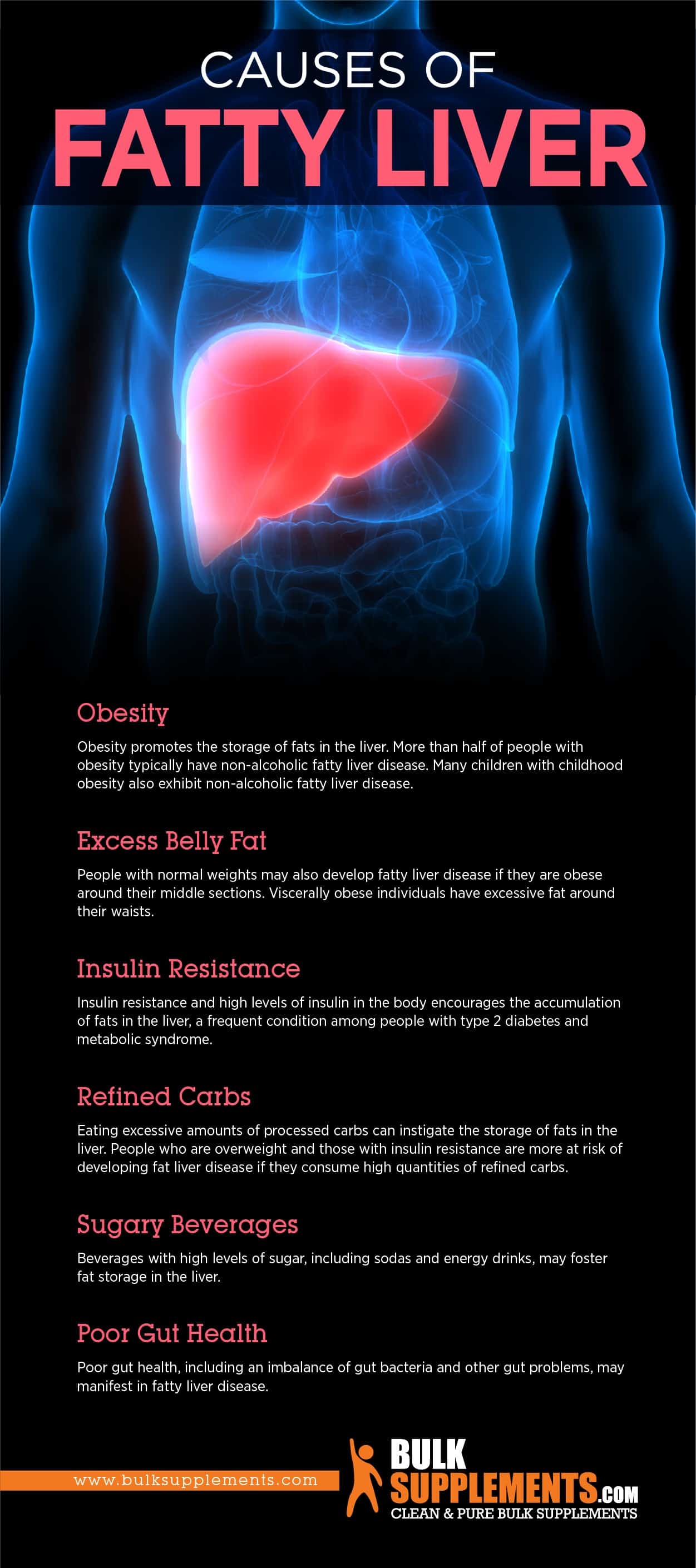
What Causes Fatty Liver Disease
Obesity
Obesity promotes the storage of fats in the liver. More than half of people with obesity typically have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Many children with childhood obesity also exhibit non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
High-Fat Diet
One of the leading causes of fatty liver disease is a high-fat diet. When you eat foods that are high in fat, your liver has to work overtime to process and break them down. This can lead to an accumulation of fat cells in your liver and eventually cause damage. To prevent this, make sure to incorporate more fruits, vegetables, and whole foods into your diet.
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance and high levels of insulin in the body encourages the accumulation of fats in the liver, a frequent condition among people with type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
Diabetes
People with diabetes are also at risk of developing fatty liver disease. High blood sugar levels can lead to an increase in fatty acids in the liver, which can eventually lead to liver damage. Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels through healthy food choices and exercise can help prevent this condition.
Alcohol Consumption
Drinking an excessive amount of alcohol can also lead to fatty liver disease. Alcohol has a direct impact on your liver, causing it to store more fat and eventually leading to liver damage and scarring. Limiting your alcohol consumption or avoiding it altogether can greatly reduce your risk of developing this condition.
Poor Diet
Our diet plays a vital role in the overall health of our body, and this includes liver health. A poor diet that is high in sugar, processed foods, and unhealthy fats puts a lot of strain on our liver, leading to fat accumulation and liver disease. On the other hand, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat proteins can promote liver health and reduce the risk of fatty liver disease.
Refined Carbs
Eating excessive amounts of processed carbs can instigate the storage of fats in the liver. People who are overweight and those with insulin resistance are more at risk of developing fat liver disease if they consume high quantities of refined carbs.
High Cholesterol
Another contributing factor to fatty liver disease is high cholesterol. When we consume a diet high in unhealthy fats, such as trans and saturated fats, it leads to increased levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol in our body. Excessive LDL cholesterol can create plaques on blood vessel walls and increase the risk of fatty liver disease. Hence, reducing the intake of high-cholesterol foods like fried and processed snacks, red meat, and full-fat dairy can help prevent this disease.
Medications and Supplements
Certain medications and supplements can also cause liver damage and contribute to fatty liver disease. Medications like corticosteroids, tamoxifen, and tamoxifen derivatives can cause liver damage over time. Supplements like bodybuilding supplements and herbal products can also cause liver damage and fat buildup in the liver. Caution should be taken when using any medication or supplement to avoid unnecessary stress on the liver.
Sugary Beverages
Beverages with high levels of sugar, including sodas and energy drinks, may foster fat storage in the liver.
Poor Gut Health
Poor gut health, including an imbalance of gut bacteria and other gut problems, may manifest in fatty liver disease.
Genetics
Finally, genetics can also play a role in the development of fatty liver disease. Some people may be genetically predisposed to developing this condition, making it even more important to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
How is Fatty Liver Disease Diagnosed
Fatty liver disease is often asymptomatic, meaning that many people don’t experience any symptoms. However, if you do have symptoms, they may include fatigue, abdominal pain, swelling in the legs, and yellowing of the skin and eyes. The best way to diagnose fatty liver disease is through imaging tests, such as an ultrasound or CT scan. These tests can reveal the presence of fat in the liver. However, physicians use various diagnostic techniques.
Medical and Family History
First, your doctor may ask about your family history, including alcohol use. It is essential to be truthful. In addition, your doctor may inquire about your current medications, eating habits and any other health conditions.
Physical Exam
A physical exam is another diagnostic tool for fatty liver disease. Your physician will weigh you and check for signs of liver damage or infection, including jaundice and enlarged liver.
Blood Tests
Blood tests further help to assess if a patient has high levels of liver enzymes, including ALT and AST. High levels of liver enzymes in the blood could indicate a problem with the liver.
Ultrasound, Computerized Tomography, or MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
Your doctor may recommend ultrasound, computerized tomography, or magnetic resonance imaging. Although imaging tests can confirm the presence of fats in the liver, they cannot be used to confirm the type of fatty liver disease.
Biopsy
A liver biopsy may be ordered if the patient shows signs of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease or associated complications, including liver cirrhosis. A liver biopsy involves taking a sample of the liver for analysis in a lab.
Can Fatty Liver Disease be Reversed?
The good news is that unlike other liver diseases such as cirrhosis or liver cancer, fatty liver disease is reversible. Reversal of the condition depends on several factors such as the stage and severity of the disease, its causative factors, and the individual’s lifestyle habits. However, in most cases, adopting healthy lifestyle habits can significantly reduce the amount of fat stored in the liver, improve liver function, and reverse the damage. Such habits include maintaining a healthy balanced diet, regular exercise, avoiding alcohol and smoking, and managing underlying health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol.
Can Fatty Liver Disease Kill You?
While fatty liver disease itself is not fatal, the complications that can arise from it can be. For example, cirrhosis can lead to liver failure, which can be life-threatening. Liver cancer can also develop as a result of fatty liver disease. In addition, those with NAFLD are at an increased risk for heart disease and stroke, which can also be fatal.
Treatment for Fatty Liver Disease
Currently, not many medicines that have been approved for the treatment of fatty liver disease. However, the right lifestyle changes may effectively reverse the condition. Surgery is necessary in some cases to treat severe complications.
Lifestyle Changes
Weight Loss
If you are obese, you should avoid eating carbs and take active measures to reduce weight. Weight loss is the leading recommended treatment option for fatty liver disease. Studies herald how it can lower the amount of fats in the liver, regardless of whether the weight loss was achieved through exercise alone or in combination with weight loss surgery.
Minimize the Intake of Refined Carbs
While many people presume that lowering one’s dietary fats suggests the easiest way to treat fatty liver disease, experts caution how less than a quarter of liver fat in people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease obtain it from dietary fats. A significant percentage of liver fat originates from fatty acids in the blood.
The body usually converts excess carbs into fats. The rate of conversion of the carbs into fat also elevates with the intake of sugar-rich foods and beverages. Thus, a diet rich in refined carbs and calories may significantly increase the levels of liver fats. For this reason, diets with lower levels of refined carbs are ideal, mainly in the form of the Mediterranean, DASH and Nordic diets.
Eat Foods That Promote Liver Fat Loss
Some foods are beneficial for liver health. For instance, foods rich in monounsaturated fats, such as olive oil, nuts and avocados may lower fats in the liver. Research further proposes how whey protein may lower levels of fat in the liver of people with obesity.
Green tea is rich in antioxidants known as catechins that correlate with lower fat levels in the liver and minimized liver inflammation. Studies also praise soluble fiber for decreasing levels of fats in the liver, lowering liver enzymes levels and generating insulin sensitivity.
Take Medicines
There are also medications that can treat fatty liver disease. These include drugs that help lower cholesterol and triglyceride levels, such as statins and fibrates. Insulin-sensitizing agents, such as metformin, can also help improve liver function and reduce fat accumulation in the liver. Doctors may prescribe medicine for insulin resistance for diabetic patients with fatty liver disease. In addition, statins may be prescribed to lessen levels of triglycerides.
Medical Procedures
In severe cases of fatty liver disease, medical procedures may be necessary. These include:
Liver transplant
In extreme cases where liver function has severe damage, a liver transplant may be necessary to restore liver function.
Bariatric surgery
For obese patients, bariatric surgery may be an effective treatment for fatty liver disease. This surgery can help promote weight loss, which can significantly improve liver health.
Supplements for Liver Health
Milk Thistle
Rich in antioxidants, milk thistle may support liver health by minimizing the production of harmful enzymes. It can further protect liver cells from chemicals and infections, enrich protein synthesis and impede the oxidation of glutathione.
The correct serving size for milk thistle is 250 milligrams per day with or without food. Avoid taking this supplement if you are pregnant or lactating. Discuss proper use with a physician prior to trying it if you have diabetes or ragweed allergies. In addition, people with hormone-related conditions or disorders of the female reproductive organs should not use milk thistle extract powder.
Side effects are uncommon, especially if you adhere to the correct dosage. If they often include nausea, headaches, indigestion and bloating. Stop supplementing with this product if the side effects worsen and seek immediate medical attention. Unfortunately, this product is not available in Finland and Sweden due to sale restrictions.
Curcumin
Curcumin offers a powerful antioxidant that can deter free radicals from bodily cells. It also supports eye, bone, digestive and cognitive health. It may assist with regulation of blood cholesterol when paired with a healthy diet and lots of exercise.
The correct dosage for turmeric extract is no more than 1,000 milligrams per day, taken with meals or water. Be careful not to spill this product on yourself or clothing because it can stain. Although side effects are rare, people with gut problems or sensitive stomachs may experience discomfort after using this product.
Talk to a doctor before using this product if you have ginger allergies. In addition, exercise extreme caution when using this product if you have diabetes, hypertension and erratic blood sugar levels. Avoid using curcumin altogether if you are pregnant or using medication for blood clotting problems.
Consider cooking with oil before consuming to promote absorption. Alternatively, mix with coconut milk before consuming.
Vitamin E
This product enriches liver and skin health since it is plentiful in antioxidants. Vitamin E also supports a host of bodily processes including cell signaling, gene expressing, fortifying the immune system.
The right dosage for this supplement is 350 milligrams per day with meals or water. Side effects from overdose are minimal. However, this product interacts with anticoagulant medications and may magnify the effects. In addition, overdose may lead to nausea, abdominal discomfort, vomiting, blurred vision, cramps, stroke and bleeding. Therefore, always adhere to the recommended dosage. Vitamin E 400 IU softgels is highly soluble in water and can be taken with shakes or juices.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are good for heart health and play a crucial role in reducing inflammation. For people with fatty liver disease, omega-3 fatty acids can reduce liver inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity. Taking an omega-3 supplement can help slow the progression of liver disease and improve overall health. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids include fatty fish, flaxseed, and chia seeds.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is essential for bone health and helps regulate immune function. People with fatty liver disease often have low levels of vitamin D, which may have a link to insulin resistance and liver inflammation. Taking a vitamin D supplement can help improve liver function by reducing inflammation and improving insulin sensitivity. Exposure to sunlight is also a great way to increase vitamin D levels.
N-acetylcysteine (NAC)
N-Acetyl L-Cysteine (NAC) is another supplement that can improve liver function in people with fatty liver disease. NAC is an antioxidant that helps reduce oxidative stress and inflammation. It has shown to reduce liver inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity in people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. NAC supplements can also improve liver function in people with alcohol-related liver disease.
The Bottom Line
The buildup of fats in the liver causes fatty liver disease. Fatty liver disease is a serious condition that can cause significant damage to your liver if left untreated. Making significant lifestyle changes, taking medication, and supplements, or undergoing medical procedures can all help improve liver function and restore your overall health. It’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the best treatment options for your specific case.
Through imaging tests, blood tests, and liver biopsy procedures, fatty liver disease can be accurately diagnosed. If you are at risk of developing fatty liver disease, making lifestyle adjustments such as eating a healthy diet, losing weight, and increasing physical activity can help prevent this condition. Stay proactive in monitoring your health and work with healthcare professionals to reduce your risk for fatty liver disease. By taking proactive steps to treat fatty liver disease, you can significantly improve your liver health and quality of life.
In conclusion, fatty liver disease is a growing concern, and it can cause serious health problems if left untreated. Supplements can play a crucial role in improving liver function and preventing liver damage. Milk thistle, vitamin E, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and N-acetylcysteine are essential supplements that can help treat fatty liver disease. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements to determine the correct dosage and ensure that they don’t interfere with any medications or preexisting conditions. By incorporating these supplements into your diet, you can support liver health and improve overall well-being.