What is a Stroke?
According to statistics published by the Center for Disease Control and Prevention, a person in the United States has a stroke every 40 seconds, which results in a death every four minutes on average. This results in about 800,000 strokes annually. The majority of these strokes are ischemic (x).
The brain is in need of a constant supply of oxygen and blood. When this supply slows down, it causes necrosis, or ‘cell death’ of brain cells.
Being able to recognize the symptoms of a stroke is very important. The faster the diagnosis, the lesser the chances of it becoming fatal. Patients who reach the emergency room within three hours from the onset of the stroke tend to be discharged soon from the hospital and are less disabled. They also tend to recover from their condition completely (x).
Strokes can occur deep within the brain or on the surface area. It all varies from individual to individual. The type of stroke depends on the location at which it occurred and the complexity.
Types of Stroke
Ischemic Stroke
Ischemic stroke occurs when blood vessels present in the neck and brain get blocked. This impedes blood circulation and oxygen supply to the brain, leading to an ischemic stroke. This is the most prevalent type and occurs in about 90 percent cases.
Hemorrhagic Stroke
Much rarer than the ischemic stroke, this appears to be present in just 10 to 15 percent of the cases, but can be responsible for up to 40 percent of deaths caused by stroke. In the case of a hemorrhagic stroke, the blood vessel ruptures, causing disruption in the blood flow. This causes the blood to leak into the brain, which builds up and compresses the brain tissue (x).
Hemorrhagic stroke has two types — aneurysm and arteriovenous malformation. An aneurysm occurs when the cerebral aneurysm bursts or due to leakage of blood vessels in the brain, causing a hemorrhagic stroke, which is a very rare type of one.
Arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is very rare and is present in a small amount of cases. With AVM, the arteries are developed abnormally and tangled, which causes the blood to be diverted away from the brain. In the cases of AVM, individuals experience bleeding in the brain.
Stroke Symptoms
If you or someone around you happens to experience any of the mentioned symptoms, seek medical treatment right away. The sooner the treatment, the better the chances of recovery.
The warning signs may disappear and fluctuate, but remember that depending on the location and the type of one and its complexity, all of these symptoms can greatly differ (x).
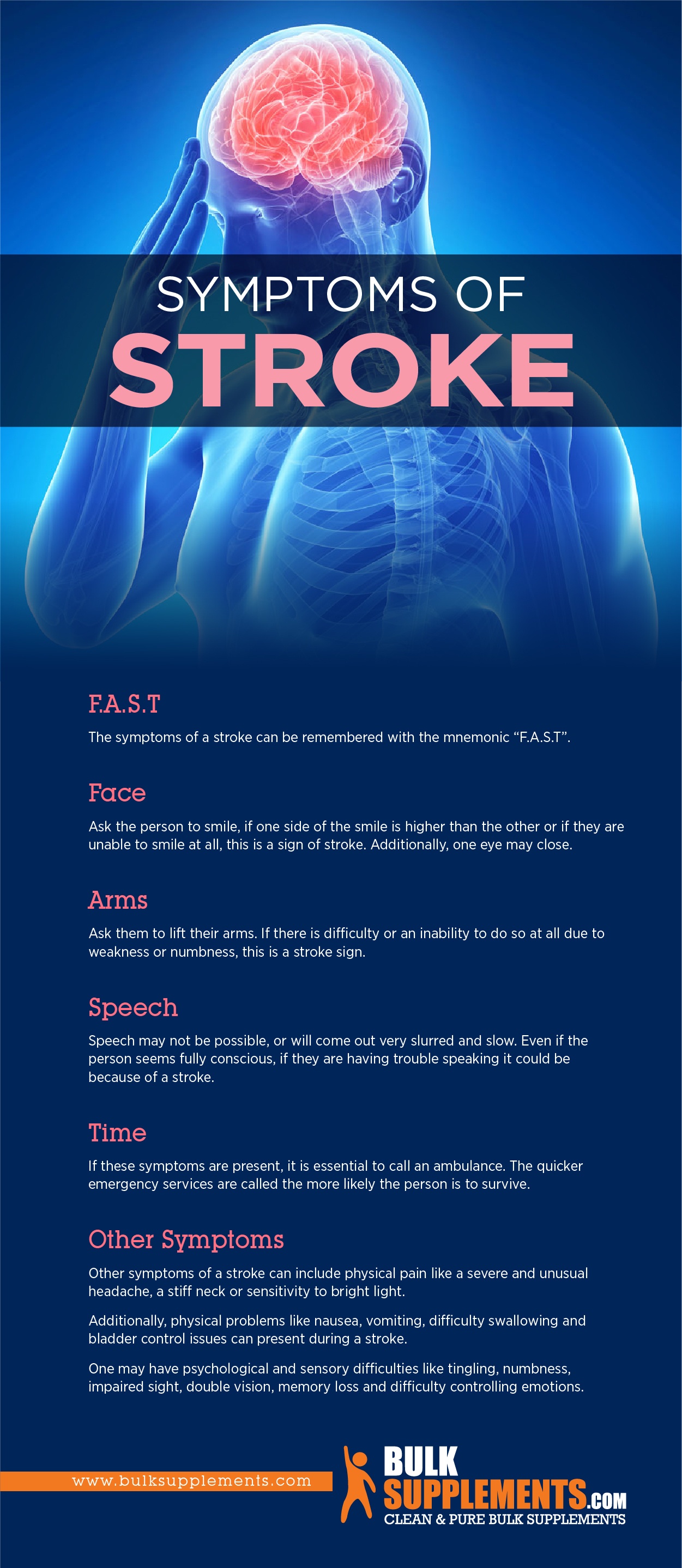
F.A.S.T
The symptoms of a stroke can be remembered with the mnemonic “F.A.S.T” (x).
Face
Ask the person to smile, if one side of the smile is higher than the other or if they are unable to smile at all, this is a sign of one. Additionally, one eye may close.
Arms
Ask them to lift their arms. If there is difficulty or an inability to do so at all due to weakness or numbness, this is also a sign.
Speech
Speech may not be possible, or will come out very slurred and slow. Even if the person seems fully conscious, if they are having trouble speaking it could be because of a stroke.
Time
If these symptoms are present, it is essential to call an ambulance. The quicker emergency services are called the more likely the person is to survive.
Other Symptoms
Other symptoms of a stroke can include physical pain like a severe and unusual headache, a stiff neck or sensitivity to bright light.
Additionally, physical problems like nausea, vomiting, difficulty swallowing and bladder control issues can present during a stroke.
One may have psychological and sensory difficulties like tingling, numbness, impaired sight, double vision, memory loss and difficulty controlling emotions (x).
Causes of Stroke
Obesity and Diabetes
Losing weight can significantly lower the levels of blood pressure and stroke. Being overweight puts you at an increased risk of a stroke along with other health issues (x).
Diabetes can damage blood vessels and it can cause the development of clots in the brain.
High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is a main cause of strokes generally, therefore by controlling it you can lower your risk of one to a great extent (x).
Atrial Fibrillation
An irregular heartbeat (or atrial fibrillation) causes clots to form in the heart. These clots start to break down and travel to the brain, which can cause one. It is possible that people with atrial fibrillation are five times more at risk of one (x).
High Cholesterol Levels
High levels of cholesterol present in the blood can lead to the buildup of plaque, thereby leading to a condition called atherosclerosis, which is a known cause of a stroke.
Misuse of Alcohol
People who consume alcohol on a daily basis are at increased risk of a stroke. There is a condition called cirrhosis that occurs due to alcohol abuse, which is associated with it (x).
Family History
A familial history of stroke is an additional risk factor. Genetics can lead to heart disorders, blood pressure issues and diabetes — all of which are factors that can cause it.
Stroke Treatment
The more you delay the supply of blood and oxygen to the brain the worse the condition may become, which can cause lifelong damage.
Treatment of stroke always depends on what type of one has taken place, the location of it and the overall health of the patient. If a person has an ischemic stroke, then medication is given to break down the clots (x). In the case of a hemorrhagic stroke, drugs are given immediately to avoid the formation of clots. Once the bleeding stops then a surgery is performed. Removal of AVM, coils, bypass and clipping can be done if needed (x).
Natural Remedies and Supplements for Stroke
Exercise
Being physically active not only improves one’s overall endurance and strength, but research suggests the risk of a stroke can be reduced to a great extent. Start small; even doing some sitting and standing can help improve the overall coordination of the body, which gets affected due to a stroke (x).
Pomegranate
After having a stroke, it is very important to lower the levels of LDL. Research suggests that taking pomegranate after one can help lower the levels of cholesterol significantly.
There are also many other benefits of pomegranate, like decreasing inflammation, fighting cancer, lowering blood pressure, improving heart health and helping with osteoarthritis symptoms. It is advised to take 750 mg twice daily to achieve the benefits of pomegranate (x).
The Bottom Line
A stroke occurs when the brain’s constant supply of blood and oxygen is reduced, which causes the brain cells to die. Strokes can occur on the surface of the brain or deep within.
The treatment of a stroke depends on the location of the stroke, the type of stroke and the overall health of the patient. The sooner one receives treatment, the higher the chance of recovery.
Some common causes of stroke include high blood pressure, diabetes, genetics and usage of drugs and abuse of alcohol. The conventional treatment includes the administration of drugs to break down the clots in order to avoid damage to the brain. In other cases, surgery is necessary to fix the issue.


