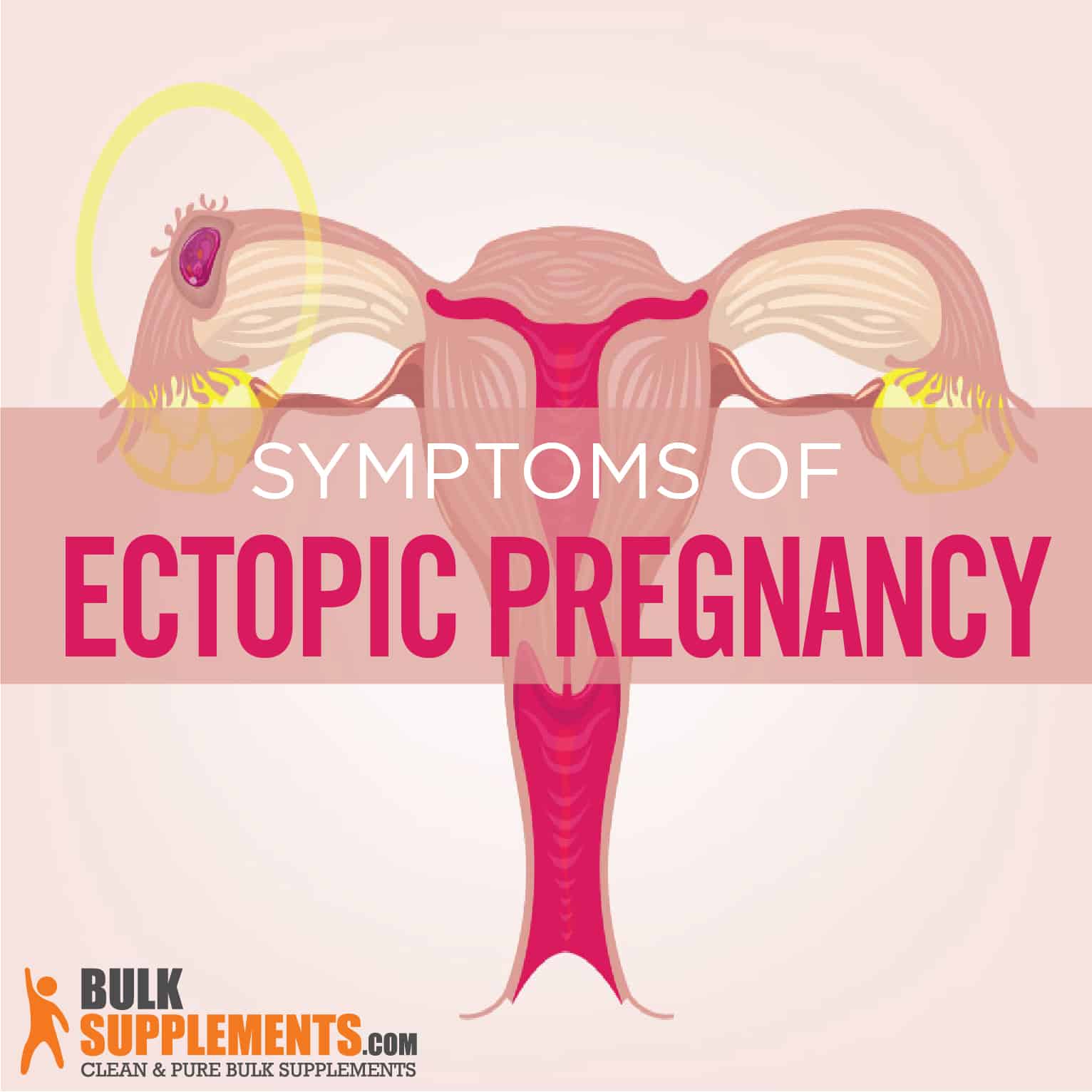
What is an Ectopic Pregnancy?
In the reproductive process, a fertilized human egg normally attaches to the wall of the uterus where it will grow into a fetus. But in an ectopic pregnancy, the egg implants itself into the wall of the fallopian tube or within the abdomen (x). Sometimes called a tubal pregnancy, an ectopic pregnancy is a grave medical condition that always results in the end of the pregnancy and can be fatal due to heavy bleeding (x). About two percent of pregnancies in the United States are ectopic (x).
Although a fallopian tube is the most common site of ectopic pregnancy, implantation also happens elsewhere. In fact, the cervix or abdomen are other locations where it commonly occurs.
An abdominal pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants at first into the fallopian tube then detaches and re-attaches to a structure or organ in the abdomen (x). These kinds of pregnancies are sometimes not caught as early as fallopian attachments.
Ectopic pregnancies usually result in the loss of the fetus. However, it is not completely impossible for an abdominal pregnancy to develop into a viable fetus. Unfortunately, the incidence rate is close to zero (x).
Frequently Asked Questions About Ectopic Pregnancy
Do Ectopic Pregnancies Show Up on a Pregnancy Test?
Yes, ectopic pregnancies cause the release of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) like normal pregnancies. Over-the-counter pregnancy tests will indicate that a woman is pregnant, although it cannot determine if the pregnancy is ectopic.
Do Ectopic Pregnancies Show on Other Tests?
Blood tests, coupled with ultrasound tests, will show an ectopic pregnancy in most cases (x).
Can You Save an Ectopic Pregnancy?
No. Ectopic pregnancy invariably results in the loss of the embryo. Moreover, it is not medically possible to transfer a fetus implanted outside the uterus into the uterus.
What Does Ectopic Pregnancy Look Like on Ultrasound?
An ectopic pregnancy on an ultrasound typically doesn’t show a structure called a gestational sac (x). If the transvaginal ultrasound doesn’t show a gestational sac while the levels of hCG are consistent with pregnancy, an ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed (x).
Can I Have an Ectopic Pregnancy After a Tubal Ligation?
The chances of getting pregnant after a tubal ligation are meager, around 1 in 1000 (x). However, the chances of having an ectopic pregnancy go up after tubal ligation (x).
Signs of pregnancy after tubal ligation include:
- Food cravings, along with cravings for particular foods
- Tenderness in the breasts
- Missed menstruation
- Unexplained fatigue
- Nausea
- Frequent urination
Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
Many women with an ectopic pregnancy experience no symptoms at all until the situation develops into an emergency due to a rupture of the walls of the fallopian tube. For those who do have symptoms, there are three common symptoms — sudden abdominal pain, a missed period and vaginal bleeding. Only half of all women with an ectopic pregnancy show all three of these signs.
Signs of Abdominal Pregnancy
Bleeding and abdominal cramps are the most common signs of abdominal pregnancy.
Heterotopic Pregnancy
Heterotopic pregnancy is the result of one fertilized egg implanting normally while, at the same time, an egg implants outside the uterus (x).
Signs of Ectopic Pregnancy at Five Weeks
- Unusual brownish spotting or light bleeding after a positive pregnancy test
- Vaginal bleeding not during your period
- Abdominal pain, usually sharp and cramping, in the lower abdomen (this usually starts as a dull ache that progresses to cramps and is worse during movement, coughing, and bowel movements)
If the ectopic pregnancy breaches a fallopian tube, you may experience any one or combination of the following:
- Heavy bleeding
- Sharp, severe abdominal pain
- Pressure in the rectum and pelvic floor
- Vomiting
- Low blood pressure
- Weakness
- Shoulder pain due to the blood in the abdomen pressing on nerves that radiate from the upper body through the pelvis (the compressed nerves send feedback back up the nerve tract, causing shoulder pain) (x)
- Stabbing cervix pain can be a harmless part of pregnancy, but it can be a harbinger of a more serious condition
Except for stabbing cervix pain, the rest of the above symptoms are a result of internal bleeding. A person experiencing severe spotting, heavy bleeding or any of the above symptoms should seek emergency medical care immediately.

Signs of Ectopic Pregnancy in Early Pregnancy
How Does Your Lower Abdomen Feel in Early Pregnancy?
Some abdominal pain is common with healthy pregnancies. Round ligament pain causes sharp, shooting pains in the hips and abdomen. These are normal (x). However, localized sharp stabbing pain on the right or left side of the abdomen could be a sign of a ruptured ectopic pregnancy (x).
A localized pain in the right ovary while pregnant or pain in the left ovary can be due to ovarian cysts. However, it is possible for ectopic pregnancy in an ovary to cause pain in the implanted ovary (x).
Is a Burning Sensation Sign of Ectopic Pregnancy?
Not on its own, but a burning and stretching sensation in the abdominal muscles is usually caused by round ligament distention (x). Pain when urinating while pregnant is most often caused by cystitis and can be treated with antibiotics (x). Mild cramping on one side of the abdomen early in pregnancy is common. However, one-sided, severe cramping can be the sign of a ruptured ectopic pregnancy (x).
The following are all common aches, pains and conditions that occur during pregnancy that do not necessarily constitute ectopic pregnancy (x):
- Breast pain
- Abdominal pain and bleeding when not on one’s period
- Vaginal cramps during early pregnancy
- Lower back pain early pregnancy
- Cramping in early pregnancy
- Uterus pain
- Pelvic pain in early pregnancy
Causes and Risk Factors of Ectopic Pregnancy
Scar Tissue
Scar tissue from previous surgeries on the fallopian tube, like tubal ligation surgery, can block or partially block the fallopian tube. These occur when a woman is attempting a post-tubal ligation pregnancy. Getting pregnant after a tubal procedure can be difficult due to the accumulation of scar tissue. The process of re-joining surgically severed fallopian tubes can also lead to significant scar tissue (x). Therefore, women who have had surgery in the abdomen, particularly in the reproductive system, are at risk. Those who had a prior ectopic pregnancy increases the chance of another one.
Many female reproductive system diseases can lead to scar tissue in fallopian tubes. Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), in particular, is the most common cause of tubal blockage. It causes significant scar tissue, as does endometriosis, another common cause of ectopic pregnancy. Note, however, that endometriosis doesn’t always lead to tubal blockage or ectopic pregnancy. Some sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) like chlamydia, gonorrhea and mycoplasma can cause severe inflammation and scarring of the fallopian tubes (x).
Inflammation
Infections can cause the fallopian tubes to swell shut. Inflammation of the fallopian tubes can also be a result of pelvic inflammatory disease, sexually transmitted diseases or endometriosis (x). Therefore, women with a history of pelvic inflammatory disease are at risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Deformity of the Fallopian Tubes
Deformity of the fallopian tubes is also a risk factor. In particular, women could have minute congenital disabilities in their fallopian tubes that prevent them from completely opening (x).
IUD
Ectopic pregnancy is also an increasing IUD pregnancy risk (x).
Diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancies are detected before the ninth week of pregnancy. To diagnose an ectopic pregnancy, a doctor will need to conduct blood tests and an ultrasound. A blood test for hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) will determine if you are pregnant or not. During the examination, the doctor uses a trans-vaginal and an abdominal ultrasound. The ultrasounds can locate the implantation point of the ectopic pregnancy, as well as determine if there is any bleeding (x).
The pregnancy tissues are removed via laparoscopic surgery. The surgeon inserts a thin scope through a small incision in the abdomen. The scope has a light and tiny camera that lets the doctor determine whether or not the fallopian tube can be saved (salpingostomy) or must be removed (salpingectomy). So, if the fallopian tube has not ruptured, a salpingostomy is usually performed. But if there’s heavy bleeding, or the fallopian tube has ruptured, a salpingectomy will be needed.
Treating Ectopic Pregnancy
If you are diagnosed with ectopic pregnancy, you may receive methotrexate for miscarriage management (x). Methotrexate helps the body absorb the fertilized egg and any other tissue from the pregnancy. It’s possible to save the fallopian tube if methotrexate is administered in time.
Ectopic pregnancy surgery is another way to save the fallopian tube. Emergency surgery is always the required treatment in this scenario.
Recovering from Ectopic Pregnancy
Physical recovery after ectopic pregnancy surgery takes about four to six weeks. Emotional recovery, however, can take longer. Therefore, emotional support groups can be a big help to recovery (x).
Helpful Supplements After Ectopic Pregnancy
Zinc
Zinc is important for a strong immune system and many essential bodily functions. In particular, zinc citrate is essential for good reproductive health (x). As a dietary supplement, take 150 mg of pure zinc citrate powder three times per day, or as directed by your physician.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that protects body tissue from the accumulation of potentially harmful chemicals caused by cellular metabolism. It is best to take one softgel (400 IU) daily with a meal, or as otherwise directed by a physician (x,x).
Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is crucial for good reproductive health. On the other hand, vitamin D deficiency is associated with preeclampsia, impaired fertility, endometriosis and polycystic ovary syndrome (x). Taking only one softgel (1250 mg) is ideal as too much vitamin D can be harmful.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is one of the 13 vitamins we must have to stay alive. In particular, it helps fetuses develop healthy nerves and nervous systems and is essential for the development of leucocytes (white blood cells) that fight infection. B12, along with iron, fights anemia that can come as a result of the heavy bleeding caused by an ectopic pregnancy. Take 100 mg to 200 mg daily, or as directed by a physician.
Folic Acid
Folic acid (Vitamin B9) is known for its ability to help prevent defects in the neural tube, part of a developing fetus’ nervous system. It’s a derivative of folate that’s also used to treat anemia in pregnant women. The CDC advises women of child-bearing age to take folic acid daily (x).
Fish Oil
The oils of cold-water fish like salmon, tuna and mackerel contain omega-3 fatty acids that are essential for good heart health (x). Omega-3 fatty acids also reduce inflammation. Try taking two fish oil softgel capsules two to three times per day.
Wild Yam Extract Powder
Wild yam extract powder is known for reducing symptoms of menopause. Take 400 mg one to two times daily, or as directed by a physician (x). However, if you have a history of hormone problems or if you are nursing or pregnant, talk to your physician before taking wild yam extract. Also, do not take this product if you are taking birth control or if you have protein S deficiency.
The Bottom Line
An ectopic pregnancy is a serious medical condition that occurs when a fertilized egg implants anywhere within a woman’s body other than the uterus. There are several causes, and it is best to avoid them as best you could. Also, taking certain dietary supplements not only help prevent the occurrence of ectopic pregnancy, but also helps promote general reproductive health.