Are you one of the 8 million Americans who suffer from cellulitis every year? If so, you already know how uncomfortable and unsightly it can be. But did you also know that good dietary practices, lifestyle changes, and even targeted natural supplements can help you take control of this skin condition in a remarkably effective way? In this blog post, we’ll discuss the causes of cellulitis, as well as treatment options to help reduce its symptoms. You’ll find out about conventional medications like antibiotics and non-medical approaches such as diet modifications – plus supplement solutions that may allow many sufferers to experience meaningful improvements in their skin health. So if expedition is what you crave then read on; learning more about your all-important first line defense against cellulitits is key to warding off infection – and celebrating a healthier life!
What is Cellulitis?
Cellulitis is a common condition that affects one in every 100 people. It is a bacterial infection that occurs when bacteria enters the skin through a cut, wound, or insect bite, causing redness, swelling, and pain. Although cellulitis is treatable, it can lead to serious complications if left untreated. If you are someone who frequently experiences skin irritations, then this comprehensive guide is perfect for you.
It is a bacterial skin infection that often affects the skin on the lower legs, but can occur anywhere on the human body. It can spread quickly and enter the lymph nodes and bloodstream, which is why it must be treated promptly. Common signs and symptoms of cellulitis include redness, swelling, tenderness, and warmth in the affected area. In severe cases, it can cause fever, fatigue, chills, and swollen lymph nodes.
Cellulitis Symptoms
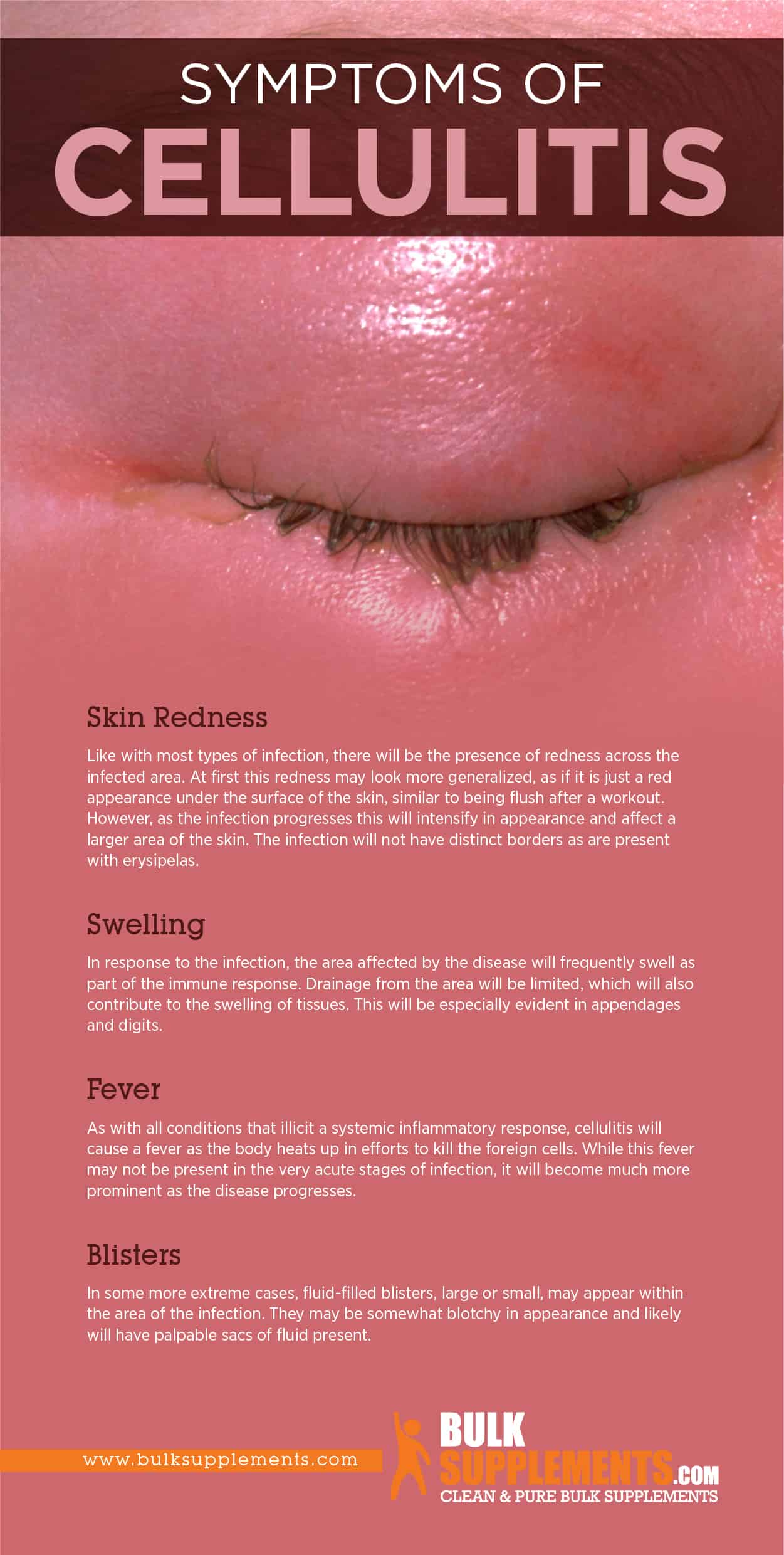
Redness
One of the first signs of cellulitis is redness, which often appears in the affected area before any other symptoms. The skin may be red and warm to the touch, and the redness may start to spread beyond the initial site of infection. If you notice any redness that seems to be spreading, especially if it’s accompanied by other symptoms, it’s best to seek medical attention right away.
Swelling
Along with redness, you may experience localized swelling in the affected area. This can make it difficult to move the affected limb or digit. If your skin feels hot to the touch, and you experience swelling, you may be experiencing inflammation of the body’s connective tissues indicative of cellulitis.
Fever
Another common symptom of cellulitis is a fever. When your body’s immune system is fighting off an infection, your temperature may rise to combat the bacterial intrusion. If you notice any significant spike in your temperature accompanied by other cellulitis symptoms, it’s best to consult a doctor immediately.
Pain
Cellulitis may cause pain and tenderness in the affected area, which may become increasingly severe as the infection progresses. You may feel a sharp, localized ache in the affected area or an intense sensitivity when you move the limb or digit, indicating cellulitis development.
Blisters
As the infection continues to progress, you may begin to experience blistering or skin damage. These blister formations are usually filled with pus, and they will often crack open if left untreated. This puts your skin at risk for further infection long-term.
Can Cellulitis Spread?
First off, yes, cellulitis can spread. Cellulitis is caused by bacteria that enter the skin through a cut, scratch, or other type of wound. Once the bacteria enter, they can quickly multiply and cause inflammation and redness in the affected area. If left untreated, cellulitis can spread to nearby skin and tissue, as well as to the bloodstream and lymph nodes. This can lead to serious complications, such as sepsis, that require hospitalization.
However, not all cases of cellulitis will spread. The risk of spreading depends on several factors, including the severity of the infection and the individual’s immune system. In mild cases, cellulitis may resolve on its own or with simple treatments like rest, elevation, and over-the-counter pain relievers. But in more severe cases, antibiotics and other medical interventions may be necessary to prevent the infection from spreading.
The key to preventing the spread of cellulitis is recognizing the symptoms early and seeking treatment as soon as possible. Symptoms of cellulitis include redness, warmth, pain, and swelling in the affected area, as well as fever and chills in some cases. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a doctor right away. They can prescribe antibiotics and other treatments to help control the infection and prevent it from spreading.
Can Cellulitis Itch?
The exact reason for cellulitis itch is not known, but there are theories that point to the body’s reaction to infection and inflammation. When bacteria penetrate the deeper layers of the skin, the immune system responds by releasing histamines and other inflammatory substances that cause itching. The itch may also be caused by the skin’s reaction to antimicrobial agents, which are commonly used to treat cellulitis. These agents can cause allergic reactions, rashes, and itching.
Other factors that can contribute to cellulitis itch include lifestyle habits, such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and stress. These factors can weaken the immune system and make it less effective in fighting off infections.
Other Forms of Cellulitis and Symptoms
Cellulitis on most areas of the skin will have a presentation with most of the symptoms listed above. However, there are some forms of cellulitis that take on a more distinct set of clinical symptoms, distinguishing it from the norm.
Periorbital Cellulitis
This type of cellulitis affects the skin around the eyes and is caused by bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus. Symptoms include redness, swelling, and pain around the eyes, as well as fever and headache. This type of cellulitis can be particularly dangerous, as it can spread to the brain and cause serious complications like meningitis. If you suspect you may have periorbital cellulitis, seek medical attention immediately.
Breast Cellulitis
This type of cellulitis is commonly found in women who are breastfeeding and is caused by bacteria entering through cracked or injured nipples. Symptoms include redness, swelling, warmth, and tenderness in the affected breast, as well as fever and chills. If you suspect you may have breast cellulitis, it is important to seek medical attention immediately to prevent the infection from spreading or causing complications like abscesses.
Orbital Cellulitis
This is an infection of the orbital tissue behind the orbital septum. The symptoms of orbital cellulitis are commonly swelling of the eyelid, redness of the eyelid and surrounding tissue, as well as discharge and discoloration. There is both pain and difficulty with eye movement. Additionally, it is likely that vision will suffer. The eyelid normally becomes noticeably swollen, projecting outwards.
Facial Cellulitis
This type of cellulitis affects the skin on the face and is caused by bacteria entering through a cut, scratch, or injury. Symptoms include redness, swelling, warmth, and tenderness in the affected area, as well as fever and chills. Facial cellulitis can be particularly dangerous, as it can spread to the brain and cause serious complications like meningitis. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you suspect you may have facial cellulitis.
Hand Cellulitis
This type of cellulitis affects the hands and is caused by bacteria entering through a cut, scratch, or injury. Symptoms include redness, swelling, warmth, and tenderness in the affected hand, as well as fever and chills. If you suspect you may have hand cellulitis, it is important to seek medical attention immediately to prevent the infection from spreading or causing complications like sepsis.
Perineal Cellulitis
This type of cellulitis affects the skin around the genitals and anus and is caused by bacteria like escherichia coli. Symptoms include redness, swelling, warmth, and tenderness in the affected area, as well as fever and chills. Perineal cellulitis can be particularly dangerous, as it can spread to the bloodstream and cause serious complications like septic shock. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you suspect you may have perineal cellulitis.
Percutaneous Cellulitis
Percutaneous cellulitis is a skin condition that occurs when bacteria enters the skin through a puncture wound. This can happen from a variety of sources, including injections and surgical procedures. Symptoms include redness, swelling, and warmth, and if left untreated, can lead to serious complications. To avoid percutaneous cellulitis, always seek medical attention if you have a puncture wound, and make sure the wound is cleaned and treated properly.
Post-Surgical Cellulitis
Post-surgical cellulitis can occur after surgery, and it’s more common in people who have weakened immune systems. The signs of post-surgical cellulitis are redness, pain, and swelling around the surgical site. If you notice these symptoms, it’s essential to contact your doctor immediately. If left untreated, the infection can spread and cause more severe complications.
Lymphangitis
Lymphangitis occurs when there is an infection in the lymphatic vessels, which are responsible for transporting lymph fluid and immune cells. The symptoms of lymphangitis include red streaks on the skin, fever, chills, and swollen lymph nodes. This type of cellulitis can be serious and requires immediate medical attention. If left untreated, it may result in sepsis, a life-threatening infection that can spread throughout the body.
Necrotizing Cellulitis
Necrotizing cellulitis, also known as flesh-eating bacteria, is a rare but severe type of cellulitis. It occurs when bacteria enter the skin through a cut or wound and spread quickly throughout the body. The symptoms of necrotizing cellulitis include redness, swelling, intense pain, blisters, fever, and chills. This type of cellulitis can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
Erysipelas
Erysipelas is another form of cellulitis that affects the skin’s upper layers and lymph vessels. It usually develops on the face or legs and appears as a reddish-blue rash with well-defined edges. The symptoms of erysipelas include pain, fever, chills, and swollen lymph nodes. If left untreated, erysipelas can spread and cause complications like abscesses, sepsis, and meningitis.
Causes of Cellulitis
Bacterial Entry Into the Body
Bacterial entry is widely considered to be the most common cause of cellulitis. The infection will commonly manifest in the area of an open wound, current or recent. This is especially common for athletes who are working out with an open wound as the moist environment and increase in body temperature will create a near perfect environment for bacteria to grow.
Most commonly, the infection is caused by the S. aureus bacteria or by a member of the streptococcal family. While both are bacterial in nature, distinguishing the exact cause through use of a careful evaluation and culture may help with outlining the best course of treatment.
Skin Breaks
The most common cause of cellulitis is when bacteria enter through a break in the skin and spread into the soft tissues beneath. This can occur through cracks, cuts, or even insect bites. People with skin conditions, such as eczema, are particularly prone to experiencing cellulitis when their skin barrier is weakened from scratching or irritation. To prevent cellulitis, always keep an eye on your skin and make sure to clean any cuts or scrapes immediately with a mild soap and warm water. You can also use a bandage or antibiotic ointment to protect the area and keep it clean.
Poor Circulation
When blood flow to the skin is limited due to an underlying health condition such as diabetes or heart disease, it can cause the skin to become weaker and more susceptible to infections like cellulitis. This is especially true for older adults who may have sluggish circulation and poor tissue oxygenation. To improve circulation, try regular exercise, avoid smoking, and manage your weight. Compression stockings or ankle pumps are also an effective way to get blood moving and reduce the risk of cellulitis.
Weak Immune System
If your immune system is weakened from a medical condition such as HIV/AIDS, cancer, or autoimmune disorders, you may be more prone to cellulitis. Your body’s natural defense against infectious bacteria is compromised, making it easier for bacteria to enter the skin through minor injuries that might not normally cause problems. To boost your immune system, get plenty of rest, eat a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and avoid contact with sick people or allergens that could trigger an immune response.
Exposure to Contaminants
Another way cellulitis can occur is by coming into contact with contaminated substances or objects such as soil, animal feces, or dirty water. People who work in certain industries such as construction or agriculture are particularly at risk for cellulitis due to their exposure to environmental contaminants. To prevent cellulitis from environmental causes, wear adequate protective clothing and make sure to clean and disinfect any wounds that occur while working.
Lymphedema
Finally, a less common cause of cellulitis is when lymph fluid accumulates in the tissues, leading to chronic swelling and an increased susceptibility to bacterial infections. This condition, known as lymphedema, can occur after lymph node surgery, cancer treatments or radiation therapy. To manage lymphedema, keep the skin clean, moisturized and avoid any injuries to the affected limb. Wearing compression garments and elevating the limb can also help to relieve swelling.
Diagnosing Cellulitis
Diagnosing cellulitis requires a physical examination by a medical professional. They will assess the location, appearance, and severity of the affected area. They may also perform blood tests to determine whether the infection has spread to your bloodstream. If the infection is severe, a biopsy of the affected skin may be necessary to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection.
In some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI may be necessary to identify the extent of the infection or to rule out other conditions such as deep vein thrombosis. Your healthcare provider may also ask you questions about your medical history, such as whether you have diabetes, a weakened immune system, or circulation problems, which can increase your risk of developing cellulitis.
Cellulitis Treatment
If you suspect that you have cellulitis, your first step should be to see a doctor. They will perform an exam and may prescribe antibiotics or recommend over-the-counter pain medication to help alleviate symptoms. In more severe cases, hospitalization may be required. But there are also some things you can do at home to improve your chances of a quick recovery. These can include rest and elevation, using warm compresses, and drinking plenty of fluids to stay hydrated.
Antibiotics
When considering cellulitis treatment guidelines, there is often a standard for using oral antibiotics as with the majority of bacterial infections. There are many antibiotics available for use, but those used specifically for treatment should be carefully considered and decided by a healthcare provider, especially for those who have antibiotic resistance of some degree.
Prevention is Key
While it’s common to hear about the best ways to treat cellulitis, prevention is equally important. You can reduce your risk of developing cellulitis by practicing good hygiene and keeping your skin healthy. This can mean washing your skin regularly, using moisturizer to prevent dryness, and avoiding sharing personal items like towels or razors. If you do get a cut or scrape, clean it promptly and keep it covered with a sterile bandage.
Warm Compresses
Applying a warm compress to the affected area can help reduce pain and swelling associated with cellulitis. Fill a clean, warm water bottle and apply it to the infected area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day. Avoid using hot water as it can burn the skin and make the infection worse.
Elevate the Affected Area
Elevating the affected area can help reduce swelling and improve blood flow, which can speed up the healing process. For example, if cellulitis has developed in your leg, try to lie down with your leg elevated on a pillow. Avoid standing or sitting for extended periods, as this can exacerbate the swelling.
What Helps Cellulitis Heal Faster?
While antibiotics are necessary to treat cellulitis, some steps can help speed up recovery and reduce symptoms.
Rest
Cellulitis is essentially a wound that needs time to heal. The body requires rest to heal effectively. Adequate sleep and time off from work will help your body use its energy reserves to combat the infection.
Stay Hydrated
Your body needs plenty of fluids to help flush out toxins and keep your immune system functioning well. Drink plenty of water and avoid dehydrating drinks like alcohol and caffeine.
Apply Moist Heat
Warm compresses can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation associated with cellulitis. Apply a warm compress to the affected area for 20 minutes, several times a day.
Home Remedies
Natural healing remedies like aloe vera, tea tree oil, turmeric, and garlic have been shown to display antibacterial properties that can help speed up cellulitis healing.
Follow Antibiotic Treatment
Antibiotics are essential to treating cellulitis. Take them exactly as your doctor has prescribed, even if your symptoms start to improve. Don’t stop taking antibiotics until you complete the full course, even if you feel better. Stopping too soon can increase your risk of recurrent cellulitis or lead to antibiotic resistance.
Supplements for Cellulitis
In addition to the textbook oral antibiotics option, several home remedies for cellulitis have shown to be effective in treating the condition, delivering satisfactory results for infection cessation. In eastern medicine, there has been a growing focus on using alternatives to antibiotics when possible. This keeps the body from developing a high degree of resistance to antibiotic medication, allowing for it to be more effective when treating bacterial diseases that do not have alternative treatment plans available.
Vitamin C
One of the key vitamins when it comes to skin health is vitamin C. This powerful antioxidant helps to protect your skin against free radicals, which can cause damage and inflammation that can lead to cellulitis. Vitamin C is also essential for the production of collagen, a protein that helps to make your skin firm and strong. You can get vitamin C from foods like citrus fruits, peppers, and broccoli. If you’re not getting enough from your diet, consider taking a vitamin C supplement for an extra boost.
Zinc
Zinc is another essential nutrient for healthy skin. It helps to promote the production of collagen, which makes your skin more resistant to infection and inflammation. Zinc also has antibacterial properties, making it useful in preventing and treating cellulitis. You can find zinc in foods like oysters, beef, and pumpkin seeds. If you’re not getting enough from your diet, a zinc supplement can help.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is important for immune system health, which is crucial in preventing and fighting infections like cellulitis. It also helps to promote healthy skin cell growth and repair. While you can get vitamin D from sunlight, many people don’t get enough through this method alone. Consider taking a vitamin D supplement to ensure you’re getting enough.
Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3s are good fats that are essential for heart health and brain function, but did you know they’re also important for healthy skin? Omega-3s have anti-inflammatory properties that can help to reduce the risk of cellulitis. You can find omega-3s in foods like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and chia seeds. If you’re not getting enough from your diet, consider taking an omega-3 supplement.
Probiotics
Probiotics are good bacteria that live in your gut and help to boost your immune system. They can also help to prevent and treat skin infections like cellulitis. You can get probiotics from foods like yogurt, kimchi, and sauerkraut. If you’re not a fan of these foods, consider taking a probiotic supplement.
Garlic
Garlic is regarded as one of the most powerful natural agents to combat bacterial and viral infections. Because of the strong properties it contains, garlic has been shown to overcome antibacterial resistant strains.
When using garlic extract powder to combat cellulitis, it is best to either consume several cloves daily while the infection is present or crush the cloves and heat in a solution, such as coconut oil, and apply it directly to the skin. The latter option is not ideal for those who have skin sensitivity as it may cause added irritation.
Turmeric
Turmeric is a powerful antibiotic and antiseptic agent that also has anti-inflammatory properties. Because of its versatility, turmeric has the potential to treat cellulitis as an infection while simultaneously combating its associated symptoms, such as swelling and inflammation.
Turmeric can be through a variety of means for medicinal purposes. It can be combined with boiled milk and drank daily, consumed daily in curcumin powder or made into a paste with honey and oil that is applied to the affected area directly on a daily basis.
Coconut
Coconut contains fatty acids that are proven to be strong antibacterial agents against a number of strains, especially the S. aureus bacterial strain that so commonly causes cellulitis. When for medicinal purposes, coconut is often an application as oil directly to the area of infection. It needs to leave it on for several hours then wash off, multiple times daily until the condition resolves.
Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar is another powerful antibacterial agent that may assist with relief from a cellulitis infection. In addition to its ability to fight the infection, apple cider vinegar powder properties will normally offer relief from itching and inflammation secondary to the infection. It is most effective when a few drops mix with water and consume daily until resolution of the infection.
The Bottom Line
While cellulitis is often has a misunderstanding as erysipelas, a healthcare provider will often be able to distinguish the difference with a visual examination. A culture of the tissue that suffers from an infection will help determine the best course of treatment moving forward, whether this is using oral antibiotics or natural supplements to combat infectious bacterial properties. Before deciding what option is best for you, make sure that you do your research about the different home remedy options available through supplements and discuss these options with your physician to make sure there are no potentially harmful side effects based on existing conditions or sensitivities you may have.
Taking supplements can be a great way to support your skin’s health and prevent infections like cellulitis. By incorporating vitamins like C and D, minerals like zinc, and nutrients like omega-3s and probiotics into your daily routine, you can give your body an extra boost in fighting off infection and promoting healthy skin. Speak to your doctor before starting any new supplements, and make sure to continue practicing good hygiene and wound care to prevent cellulitis from occurring.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease