Updated: 10/19/23
Are you considering conception, but not sure how to boost your chances? If so, male infertility supplements could be the answer. While many men may feel embarrassed asking their doctor about fertility woes, seeing a healthcare professional is necessary for finding out what specific elements may need to be addressed in terms of boosting reproductive health. From there, researching the best natural supplements that can help improve sperm quality and increases chances of conception become an important next step — this post will guide you through it all!
What is Male Infertility?
Infertility can be a complex topic, and for many couples struggling to conceive, it can be especially difficult to understand. While most people may assume that infertility is solely a woman’s issue, the reality is that male infertility affects roughly one in every seven couples who struggle with fertility.
Male infertility refers to the inability to conceive a child due to issues related to sperm function or production. This can occur for a variety of reasons, including low sperm count, abnormal sperm shape or motility, or blockages in the male reproductive system that prevent the sperm from reaching the egg. Male infertility can be a standalone issue or occur alongside other fertility factors.
One of the biggest challenges in diagnosing male infertility is that there may not be any visible symptoms or signs. However, some men may experience pain, swelling, or inflammation in the testicles or epididymis, which may indicate an issue with fertility. Additionally, if you have been trying to conceive with your partner for 12 months or longer without success, it may be time to speak with a specialist and explore testing options.
Symptoms of Male Infertility
In some cases, there are no signs or symptoms of male infertility. However, in other cases it may be caused by a set of common signs that patients may not have considered, including:
- Pain & swelling in the testicles
- Changes in desire
- Dysfunction
- Sperm health
- Testicle health
However, these signs are not specific and they may be linked to a number of other factors. For example, pain and swelling in the testicles may be a result of an infection or hernia. A male patient may experience changes in desire because of psychological factors, such as anxiety, stress or depression.
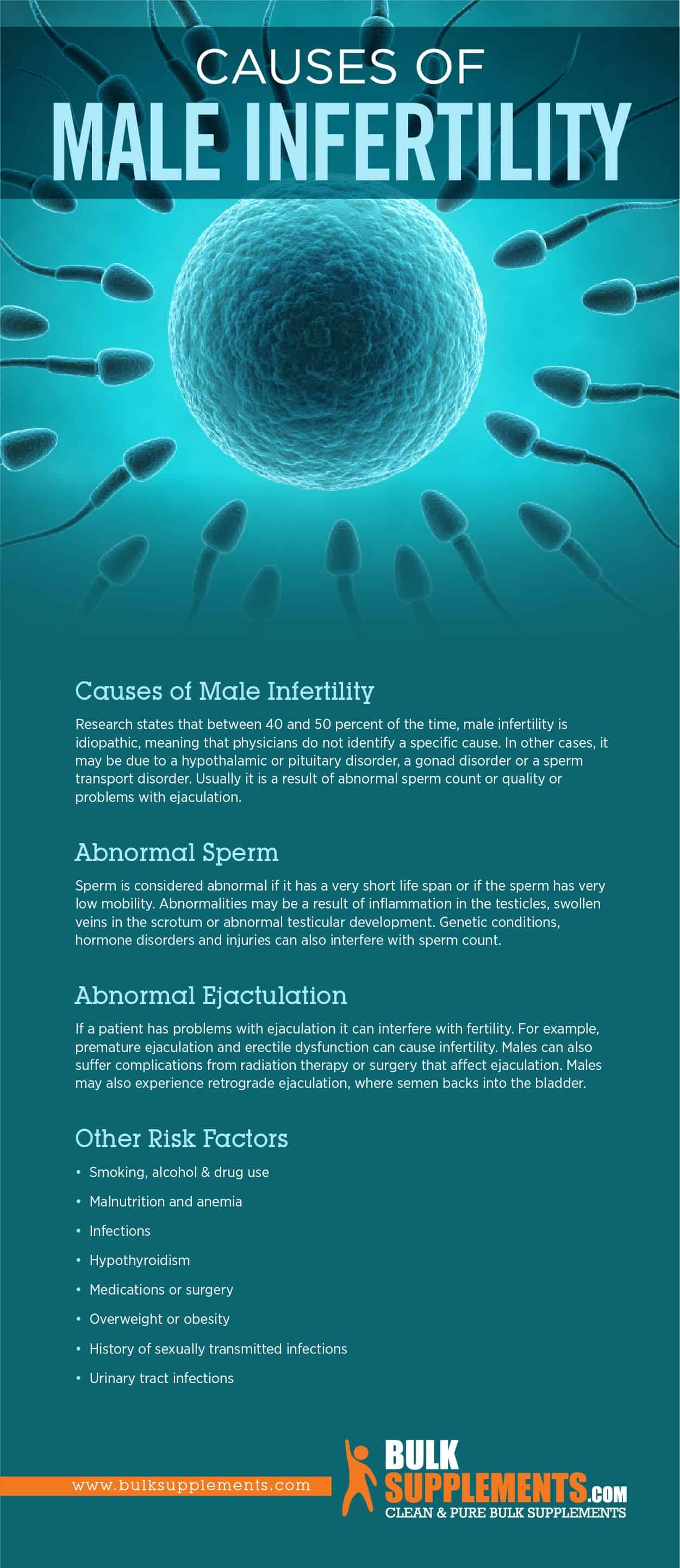
Causes of Male Infertility
Male infertility accounts for roughly 30-40% of all infertility cases. Research states that between 40 and 50 percent of the time, male infertility is idiopathic, meaning that physicians do not identify a specific cause. In other cases, it may be due to a hypothalamic or pituitary disorder, a gonad disorder or a sperm transport disorder. Usually it is a result of abnormal sperm count or quality or problems with ejaculation.
Lifestyle Habits
Lifestyle habits such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity can lead to fertility issues in men. These habits can cause disruptions to hormonal balance and cause damage to the sperm, making it harder for them to fertilize an egg. Making positive changes to your lifestyle can help improve fertility and increase the chances of conceiving a child.
Age
While women are often associated with age-related fertility problems, age can also impact a man’s fertility. As men age, the sperm count decreases, and the quality of the sperm can diminish, making it harder to conceive. It’s important to talk to your doctor about your fertility if you’re planning on having children, especially if you’re over the age of 40.
Genetic Defects
Sometimes genetic problems, such as Klinefelter Central Testicular Syndrome (KSS) or azoospermia may be the underlying cause of male infertility. In KSS, men have an extra x chromosome that can lead to smaller testicles, leading to low sperm count. In azoospermia, there is a complete occlusion or blockage of the vas deferens. For some genetic problems, IVF or retrieval of sperm can help, but always consider an expert to avoid surprises.
Exposure to Toxins
Exposure to toxins such as pesticides, heavy metals, and radiation can cause male infertility. These toxins can affect the production and quality of sperm. Men who work in industries such as chemicals, pesticides, and heavy metals are at a higher risk of exposure to these toxins.
Low Sperm Count
One of the most common causes of male infertility is a low sperm count. A healthy sperm count is typically considered to be between 15 million and 200 million sperm per milliliter of semen. If a man’s sperm count falls below this range, he may have difficulty impregnating his partner. A simple sperm analysis can diagnose low sperm count.
Poor Sperm Quality
In addition to low sperm count, poor sperm quality can also contribute to male infertility. Poor sperm quality can mean the sperm are misshapen, not moving well, or have damaged DNA. Poor sperm quality can make it difficult for sperm to penetrate and fertilize an egg.
Abnormal Sperm Morphology
Sperm morphology refers to the shape and size of the sperm. In order for sperm to be fertile, they must have a normal shape and size. If a man’s semen analysis reveals that he has a high percentage of abnormal sperm, it may be an indication that there is an underlying issue with his reproductive system. Abnormal sperm morphology can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetic abnormalities, exposure to toxins, and lifestyle factors such as smoking, drinking, and drug use.
Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction can also be a cause of male infertility. It occurs when a man has trouble getting or maintaining an erection. This can make it difficult to have intercourse and, therefore, difficult to conceive.
Testicular Pain or Swelling
Testicular pain or swelling can also indicate male infertility. Pain or swelling in the testicles can be caused by a variety of factors, including infections, varicoceles, or injury to the testicles. These conditions can affect sperm production, resulting in male infertility.
Varicocele
A varicocele is a condition where the veins in the scrotum become enlarged. This can cause a decrease in sperm production and lead to male infertility. Varicoceles can be diagnosed through a physical exam and ultrasound.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances can also contribute to male infertility. The primary male hormone responsible for sperm production. If there is a hormonal imbalance, it can affect the production of sperm and lead to male infertility.
Retrograde Ejaculation
Retrograde ejaculation is a condition in which semen is ejaculated backwards into the bladder instead of through the penis. It can occur as a result of nerve damage, medication use, or surgery. While retrograde ejaculation is not harmful, it can make it difficult to conceive a child.
History of Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can have long-lasting effects on the reproductive system, leading to infertility in some cases. STIs like chlamydia and gonorrhea can cause inflammation or blockages in the reproductive tract that could damage the sperm. If you’ve had any STIs in the past, it’s essential to notify your physician about your medical history.
Low Drive
Your drive, also known as passion, can be significantly impacted by stress, anxiety, and other lifestyle factors. However, a sudden drop in passion could be a sign of infertility. Low passion can indicate low levels of male hormones, which can directly affect sperm production. If you notice a drop in your drive, speak to a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
Overheating
The testicles are highly sensitive to temperature, and overheating them can significantly impact sperm production and quality. This is why men’s testicles are located outside the body, where they can remain a few degrees cooler than the rest of our body. Overheating can occur due to tight clothing, hot baths, or prolonged sitting. If you’re experiencing any of these, it’s essential to take steps to cool down your testicles to protect your fertility.
Anemia
Anemia is a condition that occurs when the body lacks enough red blood cells to function optimally. It is caused by a deficiency in iron, folic acid, or vitamin B12. Anemia can affect male fertility in several ways. Firstly, it can impair the body’s ability to produce healthy sperm by reducing the oxygen supply in the testicles. Secondly, it can cause decreased passion, dysfunction, and decreased fertility due to the disruption of hormonal balance in the body. Men with anemia should work on increasing their intake of iron, folic acid, and vitamin B12 through dietary changes or supplements.
Hypothyroidism
The thyroid gland is responsible for producing hormones that regulate metabolism in the body, including reproductive hormones. Any disruption of thyroid function can affect male fertility by reducing the production of male hormones or altering sperm quality and quantity. Hypothyroidism, a condition characterized by an underactive thyroid gland, is a common cause of male infertility. Men with hypothyroidism can improve their fertility through treatment with medications that help in balancing thyroid hormones.
Smoking
Smoking is one of the leading causes of male infertility. The chemicals present in cigarettes can damage the DNA in sperm and impair the ability of the sperm to fertilize the egg. Nicotine lowers the sperm density and motility while simultaneously increasing abnormal sperm morphology. Additionally, smoking can cause a decrease in male hormones levels, which can further reduce fertility. So, for couples trying to conceive, quitting smoking should be a top priority.
Obesity
Obesity can cause hormonal imbalances that affect male fertility. Excess body fat can cause an increase in estrogen levels that lead to a decrease in male hormones which in-turn lead to the production of unhealthy sperm with reduced mobility. Additionally, obesity can lead to insulin resistance, which further reduces fertility. Obese men should try to achieve and maintain a healthy weight through a combination of diet and exercise.
Can Male Infertility Be Cured?
Male infertility is a common condition that can be treated in a number of ways depending on the underlying cause. The treatment options range from making lifestyle changes, hormone therapy, surgery to assisted reproductive techniques, and alternative medicine. The most crucial step is to seek medical advice from a specialist and undergo proper testing to identify the root cause. If you have any underlying medical conditions, you may need to treat them first before receiving treatment for infertility. With proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment, many couples can overcome infertility and start a family.
Diagnosing Male Infertility
To diagnose male infertility, a doctor will ask the patient about their lifestyle and medical history to identify or rule out any risk factors that may contribute.
However, the most important test is the semen analysis. Physicians look for sperm volume and sperm count. A normal sperm volume is 2 mm and 20 to 30 million per mm is a normal sperm count range. Doctors also look at the size and shape of the sperm, which affects its ability to fertilize an egg. Sperm tests also look for sperm movement and how many active cells there are.
Physical Examination and Medical History
The first step in diagnosing male infertility is to consult a fertility specialist or urologist who specializes in male fertility. During the appointment, the doctor will perform a physical examination to check for any abnormalities in the testicles, penis, and prostate gland. The doctor will also review the patient’s medical history, including past surgeries, illnesses, medications, and lifestyle factors that could contribute to infertility. The doctor may also ask about intimate habits, including frequency, timing, and any difficulties with achieving or sustaining an erection.
Semen Analysis
A semen analysis is the most common test used to diagnose male infertility. This test involves analyzing a sample of semen under a microscope to evaluate sperm count, motility (ability to move), morphology (shape), and other factors such as volume and pH. A semen analysis may be repeated several times to confirm the results since sperm count can vary from day to day. If the results show abnormal sperm parameters, the doctor may recommend further testing to determine the underlying cause of the problem.
Hormonal Testing
Hormonal imbalances can also contribute to male infertility. The doctor may order blood tests to evaluate the levels of hormones, luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and prolactin. High levels of FSH and LH may indicate primary testicular failure or a problem with the pituitary gland that controls hormone production. Low levels of male hormones can affect sperm production and function.
Genetic Testing
In some cases, male infertility may be caused by a genetic disorder that affects sperm production or function. The doctor may recommend genetic testing to look for abnormalities in the Y chromosome, which contains genes that are essential for male fertility. The doctor may also suggest testing for cystic fibrosis, a genetic condition that can cause abnormalities in the reproductive system.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests such as ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans may be recommended to evaluate the reproductive system, including the testicles, epididymis, and vas deferens. These tests can identify structural abnormalities that may affect sperm production or transport. An ultrasound can also detect varicoceles, which are enlarged veins in the scrotum that can cause infertility by reducing blood flow and increasing testicular temperature.
Which Doctor Treats Male Infertility?
Urologist
One of the main types of doctors who treat male infertility is a urologist. These specialists are trained to treat issues with the urinary tract and male reproductive system. They are perhaps the most qualified doctors to help diagnose and treat male infertility. Urologists can help to identify blockages in the male reproductive system, low male hormone, dysfunction, and sexually transmitted infections that may be contributing to infertility.
Endocrinologist
Endocrinologists specialize in diagnosing and treating hormonal imbalances. They are particularly helpful in treating male infertility caused by issues with hormone regulation. Endocrinologists have expertise in the glandular system that generates and regulates hormones, which includes the pituitary and thyroid glands that may produce factors that interfere with the production of healthy sperm.
Andrologist
Andrologists are specialists in male reproductive organs. They help to diagnose and manage both simple and complex male reproductive issues, such as sperm count, sperm movement or morphology. They will usually assess a man’s semen quality, hormonal balance and then offer recommendations as to what the underlying issues may be.
Fertility Specialist
Fertility specialists are gynecologists or urologists who have additional training in infertility. These doctors are involved in advanced techniques, such as In Vitro Fertilization (IVF), Intrauterine Insemination (IUI), Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) and other similar techniques. They are responsible for counseling couples about their treatment options, helping to choose the most appropriate treatment, and performing the procedures themselves.
Family Practitioner or General Practitioner
Although a family doctor can’t provide all services, they can help diagnose underlying infertility issues. They would be particularly helpful when it comes to addressing the factors that may contribute to infertility causes, engagement on lifestyle changes, such as diet, exercise or health disorders that can be corrected. They can also conduct the initial evaluations and then refer their patients to the right infertility specialists, if more specific care is needed.
Male Infertility and Obesity
Obesity is a condition where your body mass index (BMI) is higher than 30. When a person is overweight, fat accumulates in different body parts, including abdominal fat. Excessive body fat leads to hormonal imbalance, causing changes in hormonal levels.
When male hormone levels are low, the production of sperm reduces, and the quality of sperm is affected. Overweight men also tend to have high levels of estrogen, which further affects the count and quality of the sperm. Such conditions increase the chances of male infertility.
Male Infertility Treatment
Physicians may be able to treat most cases of infertility with medication or surgical procedures. But ultimately treatment depends on the cause. For example, if the patient has an infection, antibiotics may help and if they have a hormone imbalance, hormone supplements may regulate them. Treatment options may be surgical or non-surgical.
Lifestyle Changes
One of the first things you can do to combat male infertility is to make lifestyle changes. This includes reducing alcohol intake, quitting smoking, reducing caffeine intake, and maintaining a healthy weight. Stock up on fresh fruits and vegetables and cut down on meat products. A diet of fruits, vegetables, lean meats, grains and legumes may help improve sperm quality. Alcohol and smoking affect sperm production and motility, and caffeine can reduce sperm count. Maintaining a healthy weight through healthy eating and exercise helps regulate hormones, which is essential for sperm production.
Researchers have not determined a specific link between sperm quality and physical fitness. However, exercise helps with weight management and there is evidence to support the connection between weight and male infertility. Moreover, exercise also helps relieve stress, which can also contribute to sperm quality. Research states that patients may improve sperm mobility and speed with moderate cardio, such as jogging.
Several studies associate sperm quality and infertility with psychological stress. Acute stress may reduce male hormonal pulsing, which affects sperm quality. Work, life events and social factors may cause patients stress that interfere with health.
Medications
While lifestyle changes are essential, it may not be enough in some cases. In that case, medical treatment can be used to treat male infertility. Prescription medication such as Clomid can stimulate sperm production, while other hormone supplements can balance hormonal imbalances. Doctors may also prescribe injectable human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) to regulate hormone levels. Other medication options include arimidex and clomiphene. These medications are prescribed on a case-by-case basis and must be taken under the strict supervision of a doctor.
Surgery
In some cases, male infertility receive treatment through surgical options. This includes varicocele surgery, which is the most common surgery for male infertility. Varicocelectomy is a common procedure to repair damaged veins in the scrotum. Varicoceles are veins in the scrotum that enlarge and can cause a reduction in sperm quality and quantity. The surgery involves rerouting the blood supply to improve sperm production. Surgeons may also perform procedures to correct obstructions that cause infertility, such as a vasectomy reversal (vasovasostomy) or epididymovasostomy. Vasovasostomy reverses a previous vasectomy to correct sperm blockage, so that it can pass during ejaculation. An epididymovasostomy clears blockage in the epididymis from previous infections, injuries or vasectomies.
Assisted Reproductive Techniques (ARTs)
If infertility treatment isn’t available or if it fails, assisted reproductive techniques (ARTs) can help a couple conceive. Depending on the cause of the patient’s infertility, a doctor may recommend:
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
IVF combines the male sperm with an over-stimulated female egg in a lab. Over-stimulating the egg with drugs produces multiple healthy eggs. The eggs grow for about three to five days and then the surgeons put the fertilized egg back into the female’s uterus. This procedure can help male infertility if the patient has a severely low sperm count.
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
This procedure, IUI, helps address low sperm count, problems with the sperm’s movement and retrograde ejaculation. The doctor inseminates the female through the uterus, injecting the sperm directly into the uterus.
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
ICSI is similar to in-vitro fertilization. Physicians use this option if the patient has very low semen quality or testicular failure that blocks sperm from the semen. The doctor uses a small needle to inject one sperm into an egg and then puts it back into the uterus after it experiences fertilization. The physician may also surgically extract sperm from the testicles or epididymis.
Alternative Therapies
Alternative medical practices can also treat male infertility, although there isn’t sufficient scientific evidence to support their efficacy. They involve using natural supplements or herbal remedies, acupuncture, and chiropractic care. While alternative treatments can be accessible and affordable, they are best as accessory treatment accompanying conventional medicine, and it’s essential to consult an expert physician before using any narrow treatment path.
Supplements for Male Fertility
Taking herbs or supplements may also improve sperm production and fertility. However, they are not an adequate medical treatment or prevention for male infertility or any other medical condition. Instead, supplements aim to improve overall health. Consult a doctor before taking any supplements.
L-Carnitine
L-carnitine is an antioxidant amino acid that may promote cardiovascular, cognitive and muscular health. Studies show that it can help with weight loss as well. It can also boost energy and athletic performance. Research studies also support its potential to improve fertility. As a dietary supplement, take L-carnitine base powder in 500 mg doses four times a day.
Zinc
Zinc contributes to immune, eye, bone and heart health. It can also help with high blood pressure and heal wounds. Zinc also helps regulate the male reproductive system (x). The recommended dosage for zinc gluconate powder is between 225 and 450 mg a day, or following a doctor’s recommendation.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 is an essential fatty acid known for its anti-inflammatory properties. This supplement is effective in increasing the blood flow to the reproductive system, improving the semen quality and increasing the circulation. Omega-3 supplements are an essential addition to your diet if you want to improve the chances of conception.
Coenzyme Q10
Coenzyme Q10 supplement enhances energy production and cellular function in the body, which is vital for producing healthy sperm. It’s an antioxidant that helps to boost male fertility by protecting the sperm cells from oxidative damage. In a study conducted on infertile men, it was found that Coenzyme Q10 supplementation improved sperm concentration and motility.
Folate
Folate, a B-vitamin, is usually associated with women’s health during pregnancy. However, research has shown that men who take folate supplements can increase their sperm count and reduce the chance of chromosomal abnormalities in the sperm. The recommended dose is 400-800mcg per day, and folic acid is the most common form of folate found in supplements.
Ashwagandha
Ashwagandha is a natural anti-inflammatory that people often use to address mental health symptoms and relieve bone and joint pain. It may also help repair damage from Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Ashwagandha is also a natural way to promote intimate health, according to studies, partly because of its ability to relieve anxiety. Take 450 mg of ashwagandha extract powder one to three times per day, unless a doctor recommends a different dosage.
D-Aspartic Acid (DAA)
D-aspartic acid comes from aspartate, an amino acid that builds proteins. It can help boost physical and athletic performance, as well as improve male hormone production and fertility. As a dietary supplement, take 2,500 to 3,500 mg of D-aspartic acid (DAA) supplement once a day with your first meal.
Maca Root
Maca root mainly grows in Peru in the Andes Mountains. Research states that it helps improve drive and fertility. Ancient cultures used it for reproduction and studies find that it may be an effective tool. The recommended dosage for maca root extract is two capsules three times a day, unless a doctor recommends a different dosage.
Fenugreek
Fenugreek is an herb that grows in India, Egypt and Middle Eastern countries. Ancient cultures used it for medicinal purposes, such as digestive issues, wound healing and even inducing labor. Studies also show that it may successfully increase drive. As a dietary supplement, take 1,000 milligrams of fenugreek powder up to three times a day, or following a physician’s instructions.
The Bottom Line
Infertility affects about one in every six couples and up to thirty percent of cases are by male infertility. Usually it does not cause any physical symptoms, but there may be signs, including pain and swelling in the testicles, dysfunction and changes in desire. There are several different factors that can cause male infertility, such as sperm count and volume, injuries and infections. The patient may also have blockages that affect fertility. Lifestyle risk factors like alcohol, drugs, smoking, diet and weight. Studies also state that infertility may be related to stress, anxiety or depression.
In many cases, the patient can receive treatment. For example, there are medications and surgical operations to increase sperm count or clear blockages. There are also assisting reproductive techniques, such as IVF or IUI that may help a couple conceive. Patients may also boost fertility or desire with natural supplements. They may improve overall health, but they are not a cure for male infertility or any other health condition. Consult a doctor for approval before starting a supplement regimen.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease


