What is Scabies?
Scabies refers to an itchy skin condition caused by small, burrowing mites known as Sarcoptes scabiei. This mite, which many refer to as the human itch mite, has eight legs and cannot be seen with the naked eye. Scabies occurs when the mite succeeds in burrowing into the skin’s top layer and starts to live and feed. The skin, in turn, reacts to the mite, which leads to the development of an extremely itchy rash. Only female mites infest humans. These female mites are usually between 0.3 mm-0.4 mm while the males are about half this size. Unlike other insects, these mites cannot fly or jump. They navigate by crawling only (x).
Scabies is mainly transmitted from skin to skin through direct contact, which implies that the mites move from an infected person to a healthy person once they come in direct contact with each other. Apart from direct contact, a number of people also interact with mites through infested items such as clothes, bedding and furniture. Basically, mites can survive 3-4 days without a human host. Thanks to this survival period, mites have a high probability of getting a host within the period. If left untreated, these microscopic insects could remain on the skin for months. Their reproduction occurs on the skin surface after they burrow into the skin to lay eggs. Next, it manifests into the formation of an itchy, red rash on the skin. Scabies precautions are essential, especially when you are visiting a new location (x).
Symptoms of Scabies
After exposure to scabies, the symptoms may not develop for up to six weeks. This duration is especially valid for people who have never had scabies before. However, if you have had a previous case of scabies, then the symptoms could develop much faster. Typically, the development of scabies symptoms in previously infected people could be between one to four days (x).
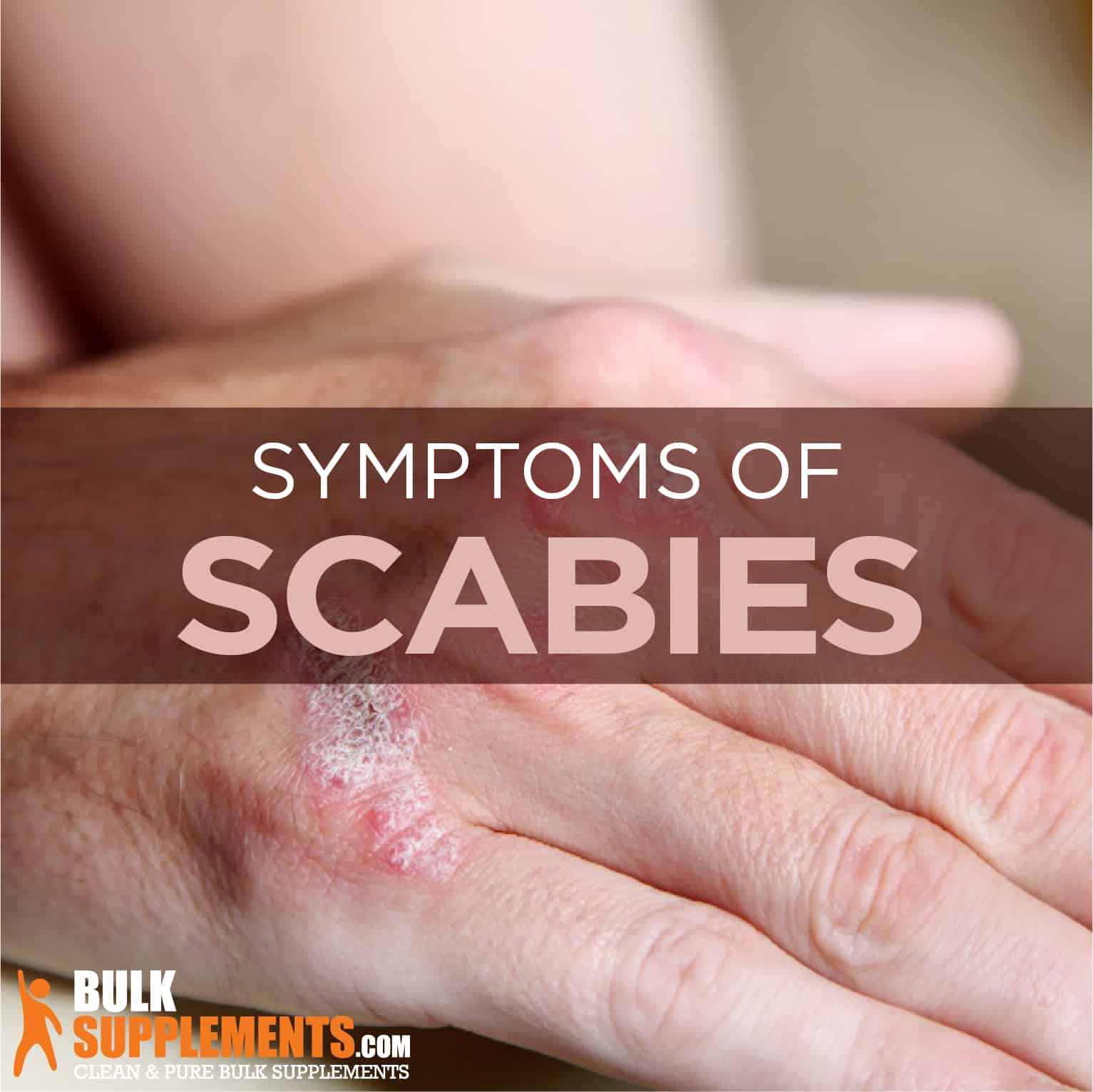
The major indicators of scabies involve a rash and intense itching that heightens at night. Vigorous and constant scratching of this area(s) could lead to an infection. In case this occurs, antibiotics for the skin infection could result. Here are some of the most common symptoms of scabies:
Itching
Itching refers to a highly uncomfortable and irritating sensation that may compel you to scratch; however, it is best not to give in to the urge to scratch. Itchy skin could come as a result of an allergic reaction or some other underlying ailment or reason. Itching remains one of the main symptoms of scabies, and it is often intense and severe. Typically, it gets worse at night or after taking a hot bath. Itchy palms and soles of feet could also denote clear indications of scabies. Similarly, itchy feet at night and the lack of any rash are mainly due to the fact that a heightened itching sensation occurs at night. Red itchy bumps on the hand could also indicate scabies (x).
Rash
Scabies is also characterized by a pimple-like skin rash — one of the most common symptoms of scabies as well. The rashes basically results from the burrowing of the mites into the skin. As the mite burrows, it forms lines or tracks. This mainly occurs in skin folds. The rashes may also look like bites, hives, knots, patches of scaly skin and pimples.
In certain cases, some people might experience blisters as well. When they appear as pimples, they are usually raised bumps with a clear top filled with fluid. Since scabies is highly contagious, mostly through direct contact and with a rash occurring often on the skin, this makes for a highly contagious condition. However, it might not start as a rash in newly infected patients. Rashes on the toes may be a symptom of scabies (x).
Sores
Sores are blister-like lesions which may appear on different parts of the body, including the cheeks, chin, lips, inside the nostril and, although quite rare, on some areas in the mouth. They usually cause an intensely painful sensation, searing pain (especially when touched) or itching before they finally burst and form crusts. In the case of scabies, these sores occur in highly infested areas that have been scratched vigorously. Open sores can lead to further infection (x).
Thickened Crusts
Typically a characteristic of crusted scabies, otherwise known as Norwegian scabies, encompasses the formation of very thick crusts, which is one of the most obvious symptoms of this scabies type. Crusted scabies refers to a very severe form whereby hundreds of thousands of mite eggs and mites themselves are found within skin crusts, thus resulting in various symptoms occurring on the skin. More often than not, the people affected by this scabies type usually possess skin with profoundly obvious thick and gray crusts, which tend to crumble when touched. Similarly, mites found in these crusts can survive for up to a week after detachment from the body (x).
Thin Grey Lines on the Skin
Mites burrow through the skin, forming thread-like tunnels of a length within the range of 10 mm. These tunnels can be viewed as grey lines on the skin and may be pretty difficult to detect or identify. These lines can be found on many parts of the body, including in between the fingers, around fingernails, armpits, waistline, inner parts of the wrists, inner elbow, soles of the feet, the breasts, particularly the areas around the nipples, male genitalia, buttocks, knees and shoulder blades. Blisters on the scalp may also be as a result of scabies and usually indicate the point at which the mite(s) began to burrow (x).

Causes of Scabies
Scabies is originally caused by an infestation of Sarcoptes scabiei mite. The female mite burrows under the skin and lays its eggs using the tunnel that it created. After about 3-4 days, the larvae move up to the skin surface and relocates/spreads to another part of the body or to a different host entirely via physical contact. Scabies can spread through direct skin to skin contact as well as through using infested towels, furniture or bedding. Even touching clothes with someone who is carrying mites could lead to a transfer of the mites to your clothes (x).
Treatment for Scabies
Treatment for scabies usually involves creams, lotions and prescription ointments to get rid of mites. There is an oral medication that a physician can prescribe as well. Due to the fact that the itch worsens at night (because the mites get more active), your doctor would most likely recommend that you apply the medicine at night. Your doctor will also likely recommend that you apply the medication on all of your skin below the neck. For medications such as creams for scabies, you can wash it off the following morning (x).
Medications for itching from it include permethrin cream, crotamiton, ivermectin and lindane lotion, among others. Permethrin cream is the most common scabies cream and it works by paralyzing and killing the mites alongside their eggs. Permethrin cream’s side effects may include skin rash, skin swelling and skin redness. Scabies shampoo is used for getting rid of mites that have burrowed under the scalp, so the itching could be more intense than on the skin. Natural remedies for scabies include tea tree oil, cayenne pepper and clove oil (x).
These also consist of some of the essential oils for treatment. Natural treatment mainly consists of using natural oils.
Supplements for Scabies
Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil remains an effective topical treatment for it due to the fact that it possesses the ability to heal skin rashes as well as relieve the itching. It is also safe for application on bedding to drive away mites (x).
Aloe Vera
Aloe vera can have a healing and soothing effect on inflamed or sunburned skin. It can also relieve itching and kill scabies. Aloe vera gel is helpful as a proactive scabies killer and so far, there is no indication of serious side effects (x).
Curcumin
Curcumin may be a cheap way to treat scabies. An experiment on a number of people with scabies showed that it had a healing rate of up to 97 percent. Similarly, it is easy to apply (x).
Zinc
While zinc may not be a direct means of treating it, Zinc is ideal for fighting the secondary infections that could stem from open wounds due to scratching (x).
Cayenne Pepper
Cayenne pepper is useful at relieving itching and pain that could result from having scabies. It may also kill the mites; however, there is no scientific evidence to support this belief yet. The capsaicin in cayenne pepper may desensitize neurons present in the skin upon topical application (x).
The Bottom Line
Scabies is a highly contagious infection. To reduce the probability of contracting scabies, it is advisable to maintain proper hygiene and disinfect regularly to ward off infection. Similarly, avoiding direct contact with people with the condition can avoid accidental infection. However, if you spot any of the symptoms mentioned in this article, contact your physician immediately.