What is Ringworm?
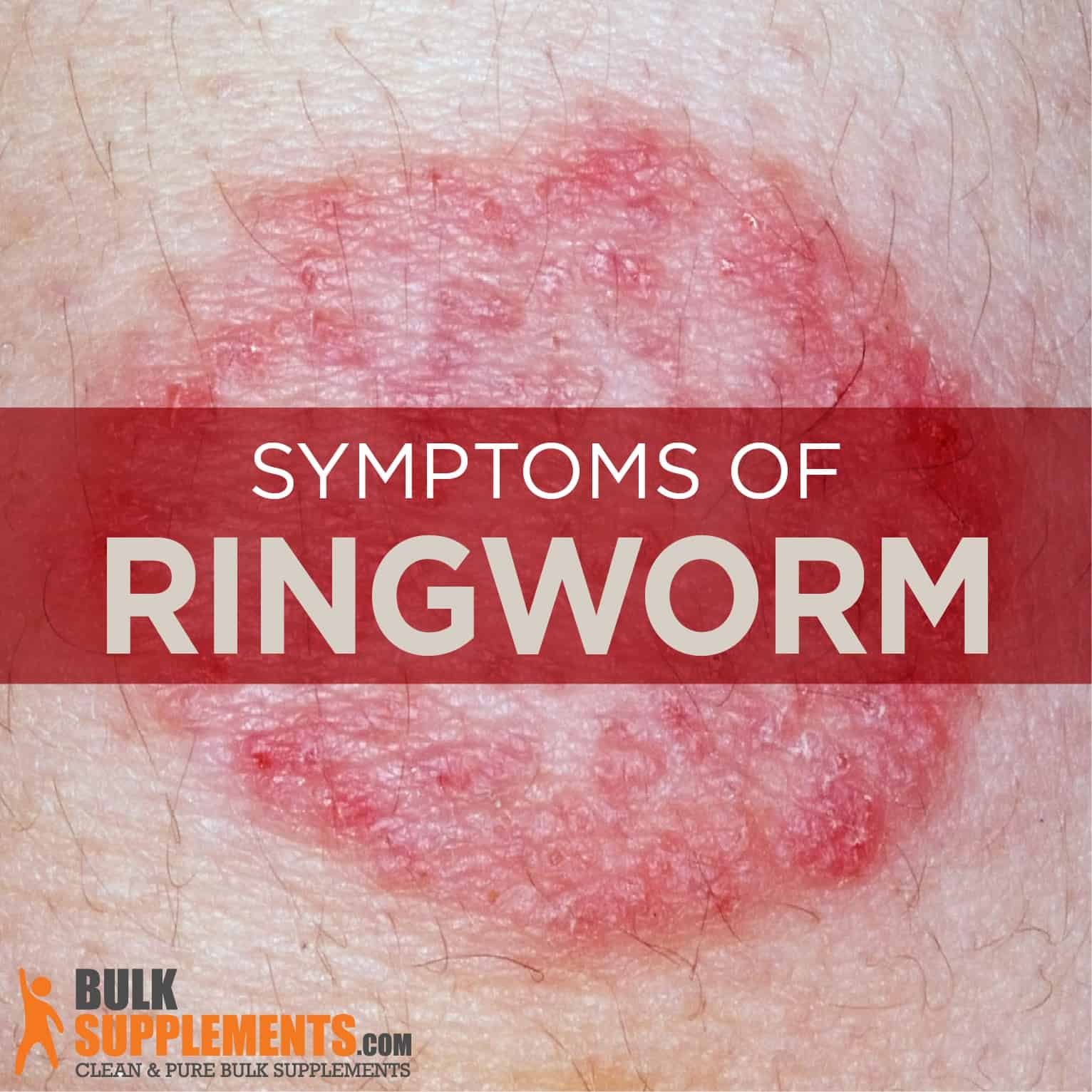
A common misconception about ringworm is that it’s caused by a worm. Believe it or not, it’s not caused by a worm at all. Ringworm, also known as tinea or dermatophytosis, is a common fungal skin infection. It can affect different parts of the body and usually develops on the top layer of the skin. The fungi that cause ringworm can live on the dead tissues of the skin, hair and nails. People can develop ringworm in these places as well as on the scalp, groin, palms and soles of the feet (x).
A ringworm infection produces symptoms on the skin such as flat, scaly lesions or red, circular rashes. It can be very itchy and uncomfortable and begin on almost any part of the body. At times, those infected may not show any obvious symptoms but still be able to spread the fungus to others (x).
Mild ringworm can be treated with antifungal medications while more-severe infections may require antifungal pills that are taken for several weeks. Some natural remedies have proven to also be effective.
Types of Ringworm and Symptoms
Ringworm can develop on the skin of almost any part of the body and has a different name depending on the part of the body affected. Its symptoms also vary depending on the infected body part. Signs usually appear between 4-14 days after the skin comes into contact with ringworm-causing fungi. With treatment, the infection can last anywhere from 2 to 4 weeks, up to several months (x, x, x).
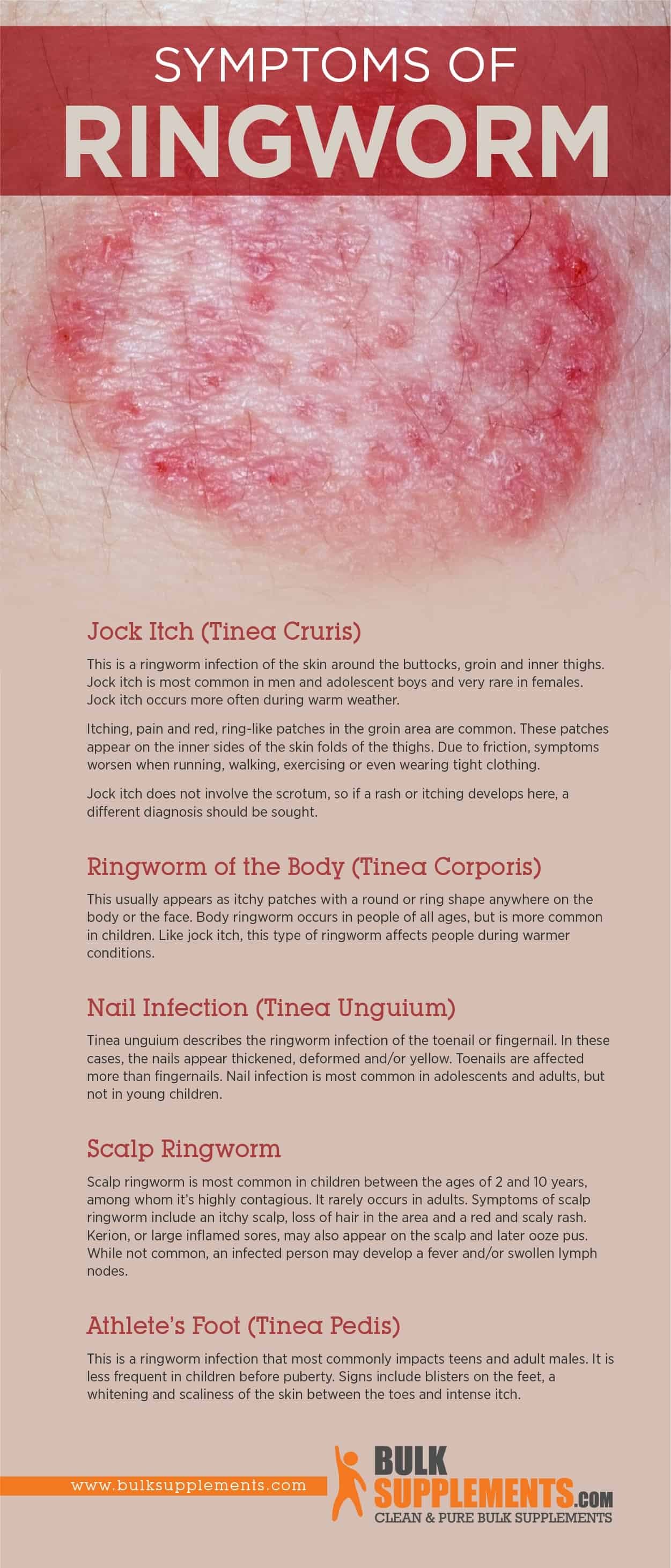
Jock Itch (Tinea Cruris)
This is a ringworm infection of the skin around the buttocks, groin and inner thighs. Jock itch is most common in men and adolescent boys and very rare in females. Jock itch occurs more often during warm weather.
Itching, pain and red, ring-like patches in the groin area are common. These patches appear on the inner sides of the skin folds of the thighs. Due to friction, symptoms worsen when running, walking, exercising or even wearing tight clothing.
Jock itch does not involve the scrotum, so if a rash or itching develops here, a different diagnosis should be sought.
Ringworm of the Body (Tinea Corporis)
This usually appears as itchy patches with a round or ring shape anywhere on the body or the face. Body ringworm occurs in people of all ages, but is more common in children. Like jock itch, this type of ringworm affects people during warmer conditions.
Nail Infection (Tinea Unguium)
Tinea unguium describes the ringworm infection of the toenail or fingernail. In these cases, the nails appear thickened, deformed and/or yellow. Toenails are affected more than fingernails. Nail infection is most common in adolescents and adults, but not in young children.
Scalp Ringworm
Scalp ringworm is most common in children between the ages of 2 and 10 years, among whom it’s highly contagious. It rarely occurs in adults. Symptoms of scalp ringworm include an itchy scalp, loss of hair in the area and a red and scaly rash. Kerion, or large inflamed sores, may also appear on the scalp and later ooze pus. While not common, an infected person may develop a fever and/or swollen lymph nodes.
Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis)
This is a ringworm infection that most commonly impacts teens and adult males. It is less frequent in children before puberty. Signs include blisters on the feet, a whitening and scaliness of the skin between the toes and intense itch.
Ringworm Causes
Three types of fungi that thrive on dead skin cells — Epidermophyton, Trichophyton and Microsporum — can cause ringworm. It often spreads by direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person. In addition, infected items such as combs, brushes or clothing can also spread it from person to person (x, x).
Touching, petting or grooming an animal that is infected also causes ringworm to spread. Dogs, cats and cows are common carriers of the fungus.
Though rare, humans can also contract ringworm by coming into contact with soil containing ringworm (x).
Risk Factors
While anyone can become infected, people with increased risk factors include those who (x):
- Have a weakened immune system
- Participate in sporting activities, such as wrestling that involve skin-to-skin contact
- Reside in areas with a warm climate
- Wear restrictive or tight clothing
- Have poor hygiene
- Are malnourished
Diagnosing Ringworm
A doctor can diagnose ringworm by examining the patient’s skin.
If the diagnosis is not clear-cut, the doctor may decide to take some skin scrapings from the affected area and examine them under a microscope. The scrapped skin can also be placed in potassium hydroxide (KOH). The KOH destroys normal skin cells and leaves the fungal cells so they can easily be viewed under a microscope.
A black light can also be used to view the patient’s skin in the affected area. If fungus is there, the affected area will glow under black light (x).
Ringworm Treatments and Remedies
Medications
Prescription and OTC topical skin medications can often clear ringworm infections in two to four weeks. Examples of medications include terbinafine (Lamisil AT) and clotrimazole (Lotrimin AF).
If the patient has ringworm of the scalp, the doctor will likely suggest a medicated shampoo as treatment (x, x).
For people with a severe infection that doesn’t respond to topical treatment, the doctor can prescribe oral medication to clear up the infection. Oral medications may have some side effects including rash, abnormal liver function and stomach upset. However, most people respond positively to some form of treatment (x).
Home Remedies
Apart from prescription and OTC medications, actions taken at home can help promote healing such as (x):
- Cleaning and drying the skin regularly
- Disinfecting the surroundings during infection by washing bedding and clothes regularly
- Avoiding clothing that can irritate the affected area
- Covering the affected area with a bandage, especially if the patient cannot avoid clothing that may irritate the area
- Trying not to scratch skin since excessive scratching can lead to a staph or strep infection like impetigo
Prevention
Practicing good hygeine goes a long way in preventing the spread of ringworm. Prevention strategies include (x, x):
- Washing hands after interaction with pets or other animals
- Wearing shoes, especially for people showering in shared areas
- Keeping feet dry and clean
- Showering and applying shampoo to the hair regularly
- Disinfecting and cleaning pet living areas, including bedding and surfaces
- Avoiding animals or people with ringworm, especially for people with a weak immune system
- Avoiding sharing personal items, such as hairbrushes or clothing with people who may have ringworm
Natural Remedies for Ringworm
Turmeric
Turmeric contains a compound called curcumin, which offers numerous health benefits including anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. Studies show it to be an effective antifungal that hinders growth of ringworm (x). For topical applications, mix turmeric extract powder with a small amount of water, then apply the paste to the affected area. As a dietary supplement, take 1,000 mg or less per day with water or a meal.
Aloe Vera
Aloe vera is also renowned for its antiseptic and antibacterial properties. It also helps control ringworm when applied topically (x). Apply fresh aloe gel or hydrated powdered extract onto the affected area three to four times daily. The aloe vera gel also has cooling properties that may help to soothe swollen and itchy skin (x).
Tea Tree Oil
This has long been used by indigenous Australians as a remedy for fungal and bacterial skin infections. Research shows that tea tree oil effectively treats ringworm (x). For ringworm treatment, apply tea tree oil that’s been diluted in a carrier oil, such as the antifungal coconut oil, directly to the affected area.
Ringworm Precautions
People should contact a healthcare provider if they experience the following (x):
- The ringworm infection progresses and gets worse
- The infection doesn’t respond to non-prescription medications
- In cases of ringworm of the scalp, which likely require prescription antifungal medication
- Discontinue any form of ringworm treatment if any side effects like negative skin reactions occur
The Bottom Line
Ringworm is a contagious fungal infection that affects the skin. Prescription or over-the-counter medications usually treat it successfully. There are also some easy hygiene-focused home treatment methods that can help prevent and speed healing of ringworm. Other remedies include the use of supplements like turmeric, aloe vera and tea tree oil.