What is Myocarditis?
Surrounding the heart is a layer of muscle referred to as the myocardium. A healthy human heart contracts and relaxes alternatively to allow the contraction and expansion of the heart chambers, which pump blood. Sometimes the myocardium may become inflamed because of reasons that doctors are yet to establish. It leads to a drastic expansion of the heart’s size, which puts a considerable amount of pressure on its chambers. It causes problems in the effectiveness of the blood-pumping process. It results in chest pain, difficulty breathing, and, in some severe cases, a heart attack. If you encounter these symptoms, you may have myocarditis. (x) It would be best if you discussed the possibility of having myocarditis with your physician.
Myocarditis affects people in various levels of severity, from mild or subtle to life-threatening. Even though the medical and scientific communities classified it as a rare disease, it affects millions of people, both adults and children, worldwide every year. In the year 2017 alone, over 3.1 million people suffered from it. (x)
Myocarditis Causes
While the exact cause of myocarditis remains unknown, doctors and scientists have found that, in most cases, it results from an infection caused by either bacteria or viruses. The inflammation that leads to myocarditis is an effect of the immune response in fighting off such infections. They include: (x) (x)
- Infections Caused by Viruses
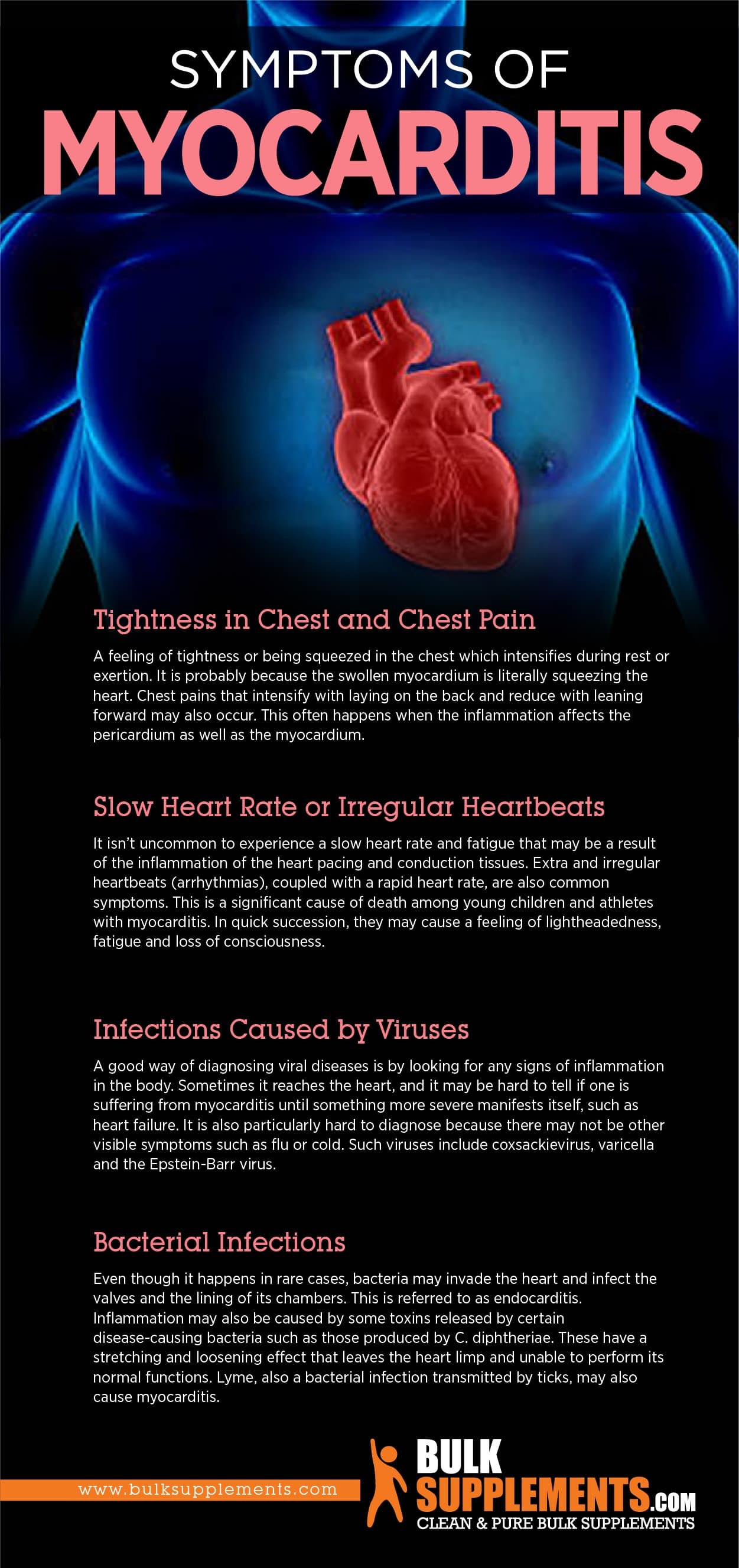
A good way of diagnosing viral diseases is by looking for any signs of inflammation in the body. Sometimes it reaches the heart, and it may be hard to tell if one is suffering from myocarditis until something more severe manifests itself, such as heart failure. It is also tough to diagnose because there may not be other visible symptoms such as flu or cold. Such viruses include coxsackievirus, varicella and the Epstein-Barr virus.
- Bacterial Infections
Even though it happens in rare cases, bacteria may invade the heart and infect the valves and the lining of the chambers. It’s referred to as endocarditis. Some toxins released by certain disease-causing bacteria, such as those produced by C. diphtheriae, may cause inflammation. These have a stretching and loosening effect that leaves the heart limp and unable to perform its normal functions. Lyme, a bacterial infection transmitted by ticks, may also cause myocarditis.
- Protozoan Infections
Trypanosoma cruzi is a protozoan transmitted through insect bites that causes inflammation of the heart muscles and, consequently, myocarditis. Those infected may develop the condition years after the incident, and if left unchecked, they may suffer heart failure.
- Other Causes
Some medicines or toxic substances introduced to the body, such as radiation, hydrocarbons, alcohol, and poison, may also cause myocarditis.
Symptoms of Myocarditis
Myocarditis has no visual symptoms, so many people have it and even recover from it without knowing it. Those more noticeable are not specific to it and appear like those of other heart problems. Their presence depends on the severity of the conditions. They include: (x)
- Tightness in Chest and Chest Pain
A feeling of tightness or being squeezed in the chest intensifies during rest or exertion. It is probably because the swollen myocardium is squeezing the heart. Chest pains that intensify with laying on the back and reduce with leaning forward may also occur. It often happens when the inflammation affects the pericardium and the myocardium. The pericardium is connective tissue, and the myocardium is the heart muscle. (x)
- Slow Heart Rate or Irregular Heartbeats
It isn’t uncommon to experience a slow heart rate and fatigue that may result from the inflammation of the heart pacing and conduction tissues. Extra and irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias), coupled with a rapid heart rate, are common symptoms. It is a significant cause of death among young children and athletes with myocarditis. In quick succession, they may cause a feeling of light-headedness, fatigue, and loss of consciousness. (x)
Diagnosis
If you suspect that you have myocarditis, see a doctor as soon as you can. Early treatment will reduce the damage to the heart muscles. Here are some tests that the doctor may perform while diagnosing the condition: (x) (x)
Electrocardiogram – This test uses non-invasive technology that makes use of electrical signals to assess your heart’s rhythm. The patterns obtained can tell the doctor whether or not you have an arrhythmia.
Echocardiogram – This is also a non-invasive technology that uses sound waves to make out images of the heart. It helps identify an inflamed and enlarged heart, a blood clot, or any issues with the valves of heart chambers.
MRI – This shows specific properties of the heart, including its size and shape. The doctor can quickly tell if there is inflammation by looking at the images.
Blood tests – A blood test will show the blood composition in terms of white blood cell count and even viruses or other pathogens that could cause infections and inflame the myocardial muscles.Chest x-ray – This is usually important in showing the size of the heart and any fluid that may be present around it.
Supplements and Remedies for Myocarditis
Handling any health concern, you may address it with vitamins, herbs, supplements or lifestyle changes. These are the best options and encouraged by top medical institutions and professionals. Talk with your health care professional first. Here are some remedies and supplements that may prevent or help treat your myocarditis:
- Carnitine
Carnitine, or L-carnitine, is a non-essential amino acid that serves as a building block for proteins in the body. It is available as a supplement for people whose natural levels are low because of disease or genetic disorders. Apart from building proteins, L-carnitine is also an essential co-factor in the transportation of fatty acids in the heart muscles.
A study using guinea pigs found that after being injected with diphtheria toxins, the carnitine levels in their heart muscles reduced drastically. (x) The rate of death decreased amongst the pigs injected with controlled amounts of L-carnitine.
The experiment with guinea pigs matches the test results in humans with diphtheria, which show an accumulation of fatty acids in the cytoplasm of the heart cells. Therefore, it suggests that the amino acid supplement could help relieve and prevent myocarditis.
In another experiment, 184 patients with diphtheria split into two groups. They administered one with controlled doses of carnitine in addition to routine treatment for four days, while they used the other as a control. At the end of the study, the researchers recorded a significant decrease in the extent of damage on the myocardial tissues and a reduced incidence of heart failure. (x)
- Vitamin C
When a virus infects the body, the immune system uses large amounts of vitamin C to fight micro-organisms. Therefore, individuals suffering from such infections have low serum levels of the vitamin.
A study included three groups of mice to investigate the effects of additional vitamin C on viral myocarditis. At the end of the study, the group administered with doses of vitamin C showed a significant improvement in their prognosis. It concluded that viruses hinder the energy production in the myocardial tissue, contributing to the inflammation. When a patient takes in some doses of Vitamin C, it protects the functioning of the mitochondrion in the myocardium, which produces energy. It boosts the metabolism in the muscles and, in the long run, reduces inflammation. (x)
- Ginger
Ginger is a natural anti-inflammatory used for decades in different parts of the world to treat many viral and bacterial infections. (x) Combine with other herbs and roots such as ginkgo and astragalus to make a remedy.
- Immune-Boosting Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Taking a nutrient-dense diet, particularly one rich in vitamins and minerals, will go a long way in relieving and preventing myocarditis. Some rich sources of such nutrients include: (x)
- Leafy greens such as spinach and kale
- Berries
- Broccoli or cauliflower
- Tomatoes
- Grapes
- Mushrooms
- Avocados
- Seeds such as chia and flax
- Green tea
- Fish
- Nuts
- Avoid Processed Foods
Processed foods and snacks often contain extraordinary amounts of salt. It aggravates myocarditis symptoms by drawing more fluids into the bloodstream, hence making the heart work harder. Such foods also contain additives, preservatives, flavors, and other substances that may increase the myocardial muscles’ inflammation. (x) Keep in mind, potassium counters salt intake, helping the body maintain its healthy level of sodium and potassium levels.
- Level the Amount of Potassium You are Taking
Potassium is a crucial compound for the body and plays a role in many vital functions. It, however, you take it in precise amounts, especially when one has heart problems. With patients taking medication to prevent heart failure, too much potassium can be disastrous. It makes the heart work harder, and considering the inflammation, this may have devastating effects. (x)
Deficient levels of potassium can increase arrhythmia. It makes it necessary to supplement with it. (x)
- Practice Hygiene
With the Covid-19 pandemic bringing your attention to the importance of personal hygiene and taking care of yourself when sick, like staying home and not spreading the infection, you most likely understand the importance of practicing hygiene. As inflammation has a connection to viral and bacterial infections, it would be advisable to practice high hygiene levels. Bacterial infections need treatment as soon as the health condition happens. It would help if you also kept some distance from people with viral diseases, especially those easily transferable. Avoid sharing body piercing instruments and always practice safe sex. You should minimize the number of sexual partners you have.
- Avoid Intense Exercise
Myocarditis may make exercise difficult, owing to the easy fatigue and shortness of breath. It would be advisable to avoid it unless cleared by the doctor. While it is a healthy habit that may help prevent inflammation and keeps your heart healthy, exercise with a delicate heart may put undue pressure on it and cause devastating effects. It is one reason athletes suddenly collapse in training. (x) (x)
Dosage
It is important to note that the FDA does not regulate carnitine, vitamin C, and ginger supplements. It leaves it to the manufacturers to recommend the best dosages for their specific products.
For the best prescription, it would be wise to visit your doctor and consult with him or her before taking any of the supplements. He will conduct a complete diagnosis and establish whether you are suffering from myocarditis. He will then prescribe the medicines, supplements or procedures to treat the condition.
Consulting with a doctor, particularly one with a good knowledge of your medical history, is essential. It helps check whether any possible interactions with any medicine you may take currently or any adverse effects because of other health conditions or even your family’s medical history.
The doctor or physician will also advise each supplement’s dosage based on various factors such as the extent of the condition, your age, and other medicines you may be taking.
Where to Buy Supplements for My Heart?
You can purchase supplements for your heart at BulkSupplements.com. The company is an industry-leading manufacturer and distributor for pure dietary supplements.
BulkSupplements.com is not just a consumer brand. It also supplies pure ingredients to other food and supplement brands to make their products. All products at BulkSupplements.com are manufactured and tested according to current and proper manufacturing practices.
Are you interested in trying any of these supplements mentioned in this article as a dietary complement for preventing heart disease? Contact BulkSupplements.com to place an order today.
The Bottom Line
Myocarditis is a disease of the circulatory system that arises from the inflammation of the heart’s myocardial muscles. The exact cause of the inflammation remains unknown and under study, but doctors and scientists associate it with viral, bacterial, and other infections transmitted through parasites.
Typically, myocarditis does not have any visible signs or symptoms, and when they show, it is usually in critical stages. They include shortness of breath, chest tightness, unexplained fatigue, light-headedness, and a doctor’s diagnosis may find some fluid around the heart. When left unchecked, myocarditis may cause heart failure, heart attacks, strokes and even death.
Some supplements and remedies for the condition include L-carnitine, vitamin C, ginger, and lifestyle changes such as eating healthy and balanced foods.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.