Updated: 9/22/23
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), also known as mononucleosis or mono, is an infection that can affect your life in many ways and take a long time to recover from. The symptoms of EBV can range from fatigue, headaches, and sore throats to fever and swollen lymph nodes. If you’ve been feeling the effects of this virus for weeks and are longing for relief, we have great news for you—you are not alone in the struggle! Read on as we dive into the causes behind EBV, offer solutions to help reduce its effect on your daily life, and more importantly provide you with our advice when it comes to fighting off this pesky virus.
What is Epstein-Barr Virus?
The Epstein-Barr virus belongs to a group of herpes viruses. It is also called herpes-virus 4. While it does have some similarities with others in its family, it also has its fair share of differences.
EBV is a common occurrence throughout the world. It typically spreads through bodily fluid exchange. It may take several weeks after getting infected for the symptoms to become noticeable. In some cases, those infected may not even notice the virus as the symptoms are mild or do not appear at all.
The most common infection caused by the Epstein-Barr virus is mononucleosis. Many believe that EBV and mononucleosis (also called ‘mono’) are the same thing, but EBV is actually one of the potential causes of mono.
Epstein-Barr virus and multiple sclerosis may also be related. Some of the other conditions possibly connected to EBV include:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease
- Type 1 diabetes
- Celiac disease
- Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
In most cases, any visible symptoms of the Epstein-Barr virus should withdraw within two to four weeks. The virus, however, won’t leave the body. It will only become dormant, which means those infected will still be a potential carrier. In rare situations, EBV can develop into the chronic active Epstein-Barr virus, which is a progressive disease that leads to the over-production of lymphocytes over an extended period.
The statistics indicate that the Epstein-Barr virus has infected about 90 percent of people in developed countries at some point in their lives. The majority of patients are typically under 25. The virus is relatively common in children.
Is Epstein Barr an Autoimmune Disease?
While EBV is not classified as an autoimmune disease on its own, it can trigger autoimmune responses in the body. When the immune system becomes activated to fight off the virus, it can mistakenly start attacking healthy tissues, leading to chronic inflammation and autoimmune disorders. Several studies have found a correlation between EBV and autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis, suggesting that this virus may be a potential environmental trigger for these conditions.
Epstein-Barr Virus Symptoms
You may not notice the symptoms right away as it often takes time for them to appear. The symptoms may not be severe, but the chances are you will notice more than a couple of them showing up simultaneously.
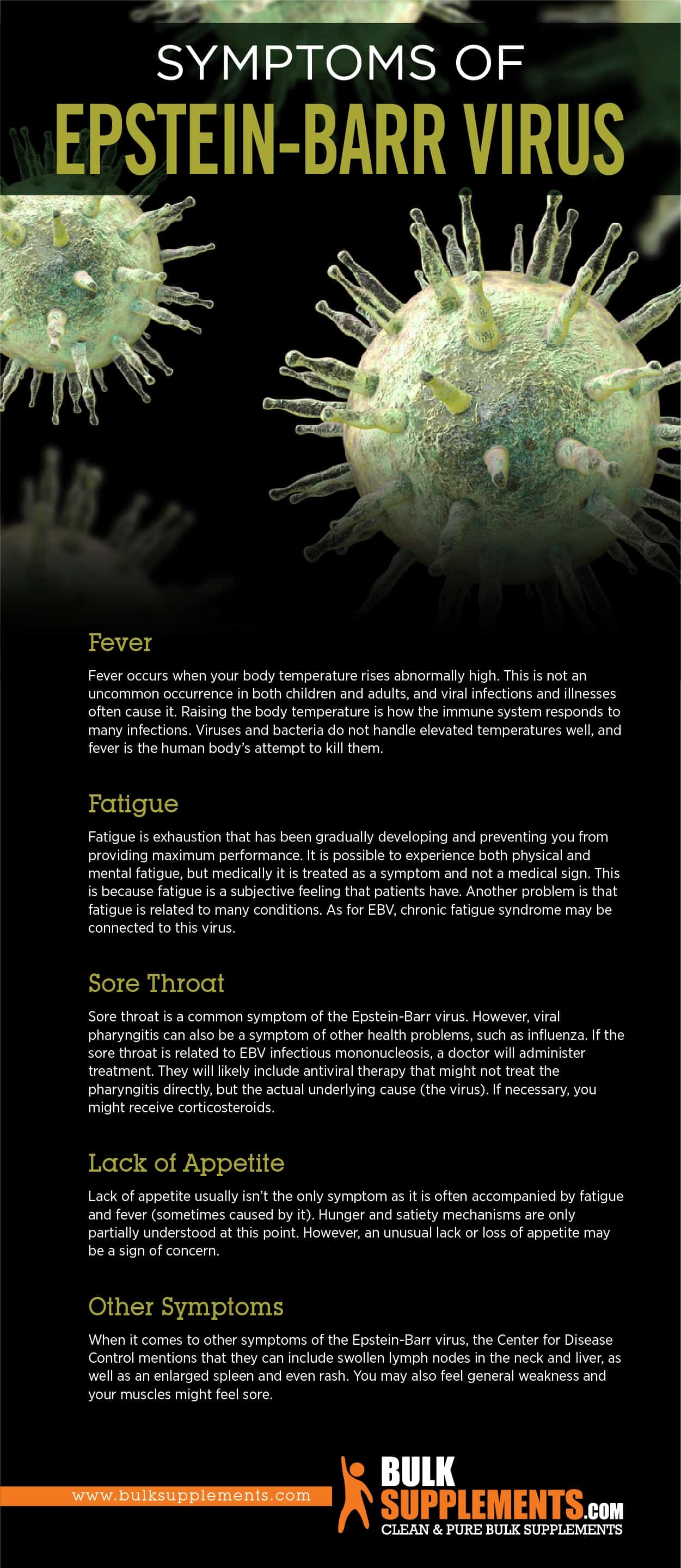
Fever
Fever occurs when your body temperature rises abnormally high. This is not an uncommon occurrence in both children and adults, and viral infections and illnesses often cause it. Raising the body temperature is how the immune system responds to many infections. Viruses and bacteria do not handle elevated temperatures well, and fever is the human body’s attempt to kill them.
Fatigue
Fatigue is exhaustion that has been gradually developing and preventing you from providing maximum performance. It is possible to experience both physical and mental fatigue, but medically it is treated as a symptom and not a medical sign. This is because fatigue is a subjective feeling that patients have. Another problem is that fatigue is related to many conditions. As for EBV, chronic fatigue syndrome may be connected to this virus (x). While the cause of CFS is still unknown, some studies suggest it may be related to EBV. Other symptoms of CFS can include memory loss, headaches, joint pain, and sleep problems. Treatment for CFS typically involves a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes.
Mononucleosis
Mononucleosis, or “mono,” is a more severe symptom of EBV. It’s caused by an immune reaction to the virus and can last from several weeks to several months. If you have mono, you may experience symptoms such as severe fatigue, fever, sore throat, swollen lymph nodes, and an enlarged spleen. Mono can be diagnosed through a blood test and usually improves with rest and hydration.
Sore Throat
Sore throat is a common symptom of the Epstein-Barr virus. However, viral pharyngitis can also be a symptom of other health problems, such as influenza. If the sore throat is related to EBV infectious mononucleosis, a doctor will administer treatment. They will likely include antiviral therapy that might not treat the pharyngitis directly, but the actual underlying cause (the virus). If necessary, you might receive corticosteroids.
Lack of Appetite
Lack of appetite usually isn’t the only symptom as it is often accompanied by fatigue and fever (sometimes caused by it). Hunger and satiety mechanisms are only partially understood at this point. However, an unusual lack or loss of appetite may be a sign of concern.
Other Symptoms
When it comes to other symptoms of the Epstein-Barr virus, the Center for Disease Control mentions that they can include swollen lymph nodes in the neck and liver, as well as an enlarged spleen and even rash. You may also feel general weakness and your muscles might feel sore.
What Causes Epstein-Barr Virus?
The Epstein-Barr virus is present in bodily fluids. Contact with the infected saliva, blood or semen can make you a carrier. It is vital to note that those with a weak immune system may have a higher chance of getting infected.
Kissing and sex are two of the main ways that humans exchange bodily fluids. Although it may be less likely, it is possible to become infected by using the same glass as an EBV carrier.
The above mentioned causes might be the most common, but EBV also has some other risk factors (using someone else’s toothbrush, for example). Less commonly, it is possible to contract the virus through an organ transplant or via a blood transfusion.
Epstein Barr and MS
EBV is a herpes virus that infects more than 90% of the world’s population. It is usually acquired in childhood and remains dormant in the body for life. However, in some cases, the virus can reactivate and cause a range of health problems, including mono, Hodgkin’s lymphoma, and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Recently, researchers have found that EBV may also play a role in the development of MS. In fact, studies have shown that people with MS have higher levels of EBV antibodies in their blood compared to those without the disease.
One theory is that EBV may trigger an autoimmune response in the body, leading to MS. This means that the body’s immune system mistakenly targets and attacks its own cells and tissues, including the nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. Researchers believe that EBV may cause the immune system to become overactive and attack these cells, leading to the symptoms of MS.
While the link between EBV and MS is still being studied, there are some indications that treating EBV may have a positive impact on MS symptoms. For example, one study found that treatment with an antiviral medication called valacyclovir reduced MS symptoms in some patients. The medication works by targeting the virus and reducing its ability to replicate. However, more research is needed to determine whether antiviral medication can effectively treat MS.
Epstein Barr Diagnosis
Epstein Barr is typically diagnosed through a blood test which will search for the presence of antibodies in the bloodstream to the virus.
If a patient has symptoms of mono, a doctor may use additional tests such as a physical exam or check for viral particles in your blood. In some cases, more complicated testing may be needed to rule out other illnesses that may mimic the symptoms of mono.
How to Read Epstein-Barr Test Results
Interpreting EBV test results can be tricky since each person’s immune response to the virus can vary. However, in general, if your IgM antibody levels are high, it indicates that your infection is recent or ongoing. Elevated IgG antibody levels typically indicate that you’ve had the virus in the past. However, it’s worth noting that the presence of IgG antibodies alone doesn’t necessarily mean that you’re immune to the virus. In some cases, the virus can reactivate and cause symptoms even in people who have previously been infected.
Additionally, healthcare providers may look at the ratio of IgM to IgG antibodies to determine the stage of infection. A high level of IgM antibodies relative to IgG antibodies could indicate an acute infection, while a high level of IgG antibodies relative to IgM antibodies may suggest a past infection. However, other factors, such as the timing of the test, can also affect the results.
What Kills Epstein-Barr Virus?
One of the most effective ways to address a chronic EBV infection is to support your body’s immune system. A diet rich in whole, organic foods, and free of processed sugars and refined carbohydrates, can help to fuel your immune response and reduce inflammation. Incorporating immune-boosting foods like bone broth, dark leafy greens, and fermented vegetables, and avoiding common food sensitivities like gluten, dairy, and soy can aid in the healing process.
Epstein-Barr Virus Treatment
Antiviral Medications
Antiviral medications are drugs that can destroy viruses in the body. They can help reduce the symptoms of EBV, including fatigue, fever, and sore throat. Some common antiviral medications used to treat EBV include acyclovir, famciclovir, and valacyclovir. These medications work by slowing down the spread of the virus, reducing the symptoms and duration of illness. However, it is important to note that these medications are most effective when taken as soon as possible after symptoms begin.
Over-The-Counter Pain Relievers
Over-the-counter pain relievers are medications that are available without a prescription. They can help to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation caused by EBV. Some common over-the-counter pain relievers include acetaminophen, ibuprofen, and aspirin. These medications should be used only as directed and with caution, especially if you have a history of liver or kidney problems, or if you are pregnant.
Immunoglobulin (IVIG) Therapy
This treatment involves introducing EBV-neutralizing antibodies into the bloodstream to fight the virus. IVIG therapy is highly effective in controlling and treating chronic infections caused by EBV. Additionally, this treatment is relatively safe and is often used for pediatric patients with primary immunodeficiency diseases.
Rest
Rest is one of the most important treatments for EBV. Resting allows your body to recover and increases your chances of avoiding long-term complications. You should try to get at least eight hours of sleep each night and avoid strenuous activities until you feel better.
Epstein-Barr Virus Remedies and Supplements
Specific EBV therapy doesn’t exist. However, there are ways to treat the symptoms and provide relief until the virus becomes dormant. Apart from getting a lot of rest and drinking plenty of fluids, you can consider some of the following supplements.
Vitamin C
Many consider vitamin C to be a crucial nutrient that can have multiple positive benefits on human health. It is primarily known for having strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Vitamin C could play a crucial role in fighting flu and colds. It may also help to reduce fatigue, which may be of vital importance to those with EBV.
Other positive effects of vitamin C, which is also known as ascorbic acid, include boosting brain, bone and skin health, as well as improving your mood and preventing cognitive decline.
The recommended dosage of vitamin C differs for healthy persons and those whose immune system is under attack. If you want to support your immunity, you can go with the dosage of 1,000 mg daily or as agreed with your physician. If the powder is not your preferred choice, you can also use ascorbic acid capsules.
L-Lysine
Lysine is an essential amino acid that participates in the creation of proteins that help to strengthen your immune system. Many studies suggest that lysine can help to treat HSV-1, which is also a form of herpes. Lysine also has anti-inflammatory properties and can contribute to boosting your appetite.
When it comes to the recommended dosage, you should aim to take up to two capsules per day, which is 1,000 mg per day, or as directed by your physician. If the tablets are not your preferred way of taking lysine, you may also try the powdered version. Please note that you should consider taking lysine with other amino acids to optimize their effectiveness. If you take only lysine, you may compromise the effects of other amino acids.
Astragalus
Astragalus is an herb with a long history of use in traditional medicine in countries like China. Packing a ton of antioxidants, astragalus is believed to have immune-enhancing properties that may make it useful in fighting EBV. Astragalus is available in powder, capsule, and liquid tincture form.
Berberine
Berberine is a plant-sourced compound that is available in powder form. This particular formula was derived from the philodendron plants and contains additional HCL to improve absorption. The main reason why it could assist in treating mono and EBV symptoms is that it has antiviral properties that have proven particularly helpful in dealing with the herpes simplex virus.
The potential benefits of berberine do not stop there. The supplement can also assist in optimizing blood pressure, cholesterol and blood sugar levels. Additionally, it can support your immunity with the anti-inflammatory properties.
The recommended dosage of berberine is 1,000 mg per day unless your physician directs otherwise. Please note that you shouldn’t use the supplement for over three months unless your doctor approves.
Echinacea
Echinacea is a herb that has antiviral characteristics which may promote your immunity and help to deal with the EBV virus. The herb contains echinacoside, which has been shown to stimulate the immune system and help the body fight off viruses. The recommended dosage for echinacea is 450-900 mg per day.
Olive Leaf Extract
Olive leaf extract is a compound that has multiple benefits, including preventing virus replication and having antibacterial properties. That may help to deal with other bacteria to help the immune system to focus on dealing with EBV. The recommended dosage for olive leaf extract is 750 mg per day.
Reishi Mushroom
Reishi mushroom is a fungi with immune-boosting properties that have been shown to be effective against EBV. The mushroom contains polysaccharides and beta-glucans that stimulate the immune system and help the body fight off viruses, including the EBV virus. Reishi Mushroom can be consumed in the form of tea, supplements, or capsule
Beta-Glucan
Beta-glucan is a type of soluble fiber found in certain foods, including oats, barley, and mushrooms. Beta glucan can support the optimal functioning of the immune system, which may be vital in resisting infection. It works by activating and enhancing the immune system’s response to pathogens, including viruses. Stick to 250 mg of beta glucan as the daily dosage.
The Bottom Line
Epstein-Barr virus is from the herpes virus family and is transmitted through bodily fluids. You should contact your doctor if you are suspecting mono caused by EBV. They can arrange a test for mononucleosis to confirm the diagnosis. Most health professionals will conduct simple blood tests to establish EBV or mono.
If the diagnosis of the Epstein-Barr virus has been confirmed, prepare to be inactive for a couple weeks. During that period, you will treat the symptoms to experience relief and ensure that you stay hydrated. In most cases, EBV will withdraw and go dormant within two to four weeks. It is vital to note that you should rely on your doctor and contact them at any point when you have a medical concern.
In conclusion, EBV is a common virus that can cause a range of health problems, and there are currently no known cures for it. However, herbal remedies and vitamin & mineral bulk supplements can help support immune health and prevent the virus from causing more harm. By incorporating these natural remedies into your daily routine and making certain lifestyle changes, you can boost your immune system and reduce the risk of EBV complications. Remember to always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements and follow their instructions carefully to ensure safety and effectiveness.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease